
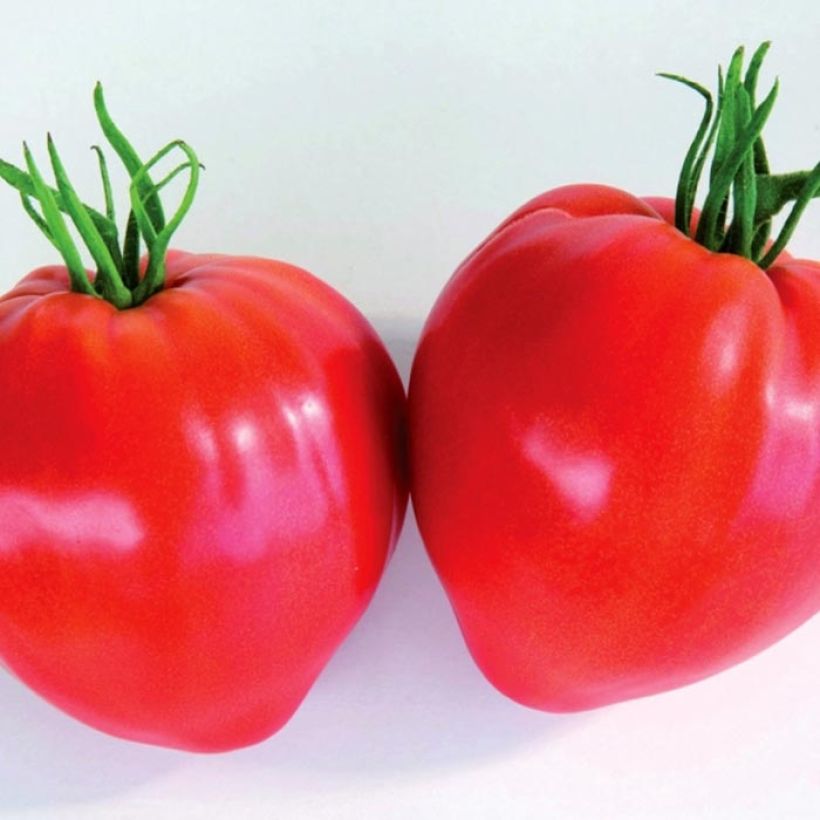
Tomate Cauralina F1 en plant GREFFE
Tomato Grafted Cauralina F1 Tomato Plants
Solanum lycopersicum Cauralina F1
Tomato
Special offer!
Receive a €20 voucher for any order over €90 (excluding delivery costs, credit notes, and plastic-free options)!
1- Add your favorite plants to your cart.
2- Once you have reached €90, confirm your order (you can even choose the delivery date!).
3- As soon as your order is shipped, you will receive an email containing your voucher code, valid for 3 months (90 days).
Your voucher is unique and can only be used once, for any order with a minimum value of €20, excluding delivery costs.
Can be combined with other current offers, non-divisible and non-refundable.
This plant carries a 6 months recovery warranty
More information
We guarantee the quality of our plants for a full growing cycle, and will replace at our expense any plant that fails to recover under normal climatic and planting conditions.
Description
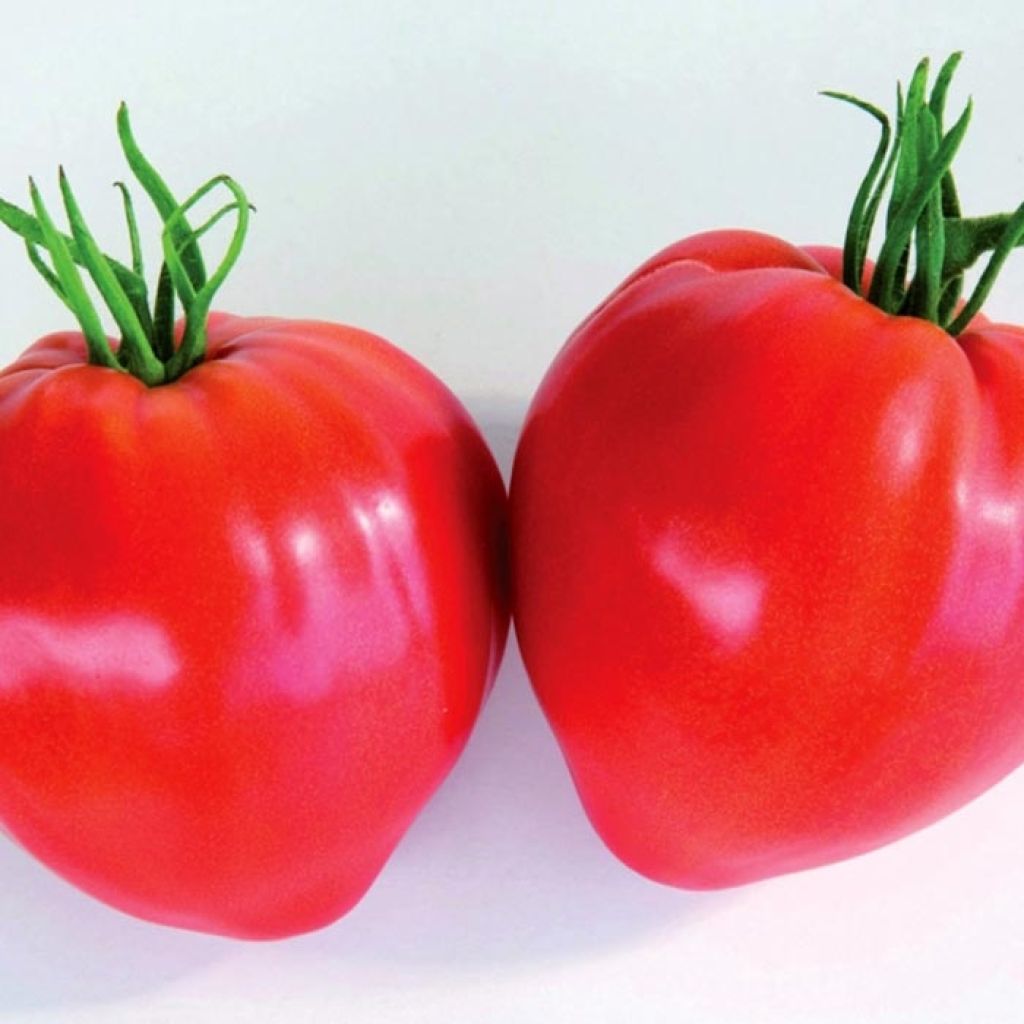
The Cauralina F1 Tomato, a beefsteak type, is a variety that produces regular, heart-shaped fruits weighing 160 to 200 g each, with a vibrant coral red color when ripe, and a consistent size and shape. Their flesh is dense and of excellent taste quality, making them ideal for use in salads, juices, gazpacho, and perfect for stuffing. The Tomato is a tender plant that is grown as an annual, requiring heat and nutrient-rich soil. Grafted plants of the Cauralina F1 Tomato should be planted from April to June, after the last frost, for a harvest from July to October.
The grafting technique involves giving a desired variety (in this case, 'Cauralina F1') the root system of another specially selected variety, known as the rootstock. This rootstock has excellent resistance to soil parasites and diseases, which provides additional vigor to the plant: it becomes more resistant to challenging external conditions (such as cold climates) and yields significantly higher than a non-grafted plant. The fruiting of grafted plants starts earlier and lower on the main stem. Thanks to the use of the 'Protector' rootstock, our grafted tomato plants also produce fewer leaves, making ripening and harvesting easier.
The Tomato originates from South America and Central America. Several varieties were already cultivated by the Incas long before the arrival of the Conquistadors. The term "Tomate" comes from the Inca Tomatl, which refers to both the plant and the fruit it produces. It is one of the many foods that came to us from the New World, along with beans, corn, squash, potatoes, and chili peppers. The Tomato took significantly longer to reach our taste buds. For a long time, it was cultivated for its aesthetic and medicinal qualities but was considered toxic due to its resemblance to the fruit of the Mandrake, another member of the Solanaceae family. It only became a regular part of our diets in the early 20th century.
The Tomato is a herbaceous perennial plant in tropical climates, but it is grown as an annual in our latitudes. It lignifies over time and produces small, insignificant yellow flowers grouped in clusters, which will eventually turn into fruits. Tomatoes can be grown in open ground but can also be cultivated in containers on a balcony, with a preference for compact varieties.
Tomatoes are a fruit with numerous nutritional benefits. Low in calories like most vegetables, they are rich in water and contain a molecule of great interest: lycopene, a powerful antioxidant. They are also rich in vitamin C, provitamin A, and trace elements.
In terms of cooking, Tomatoes can be eaten raw or cooked in many different ways: in salads or as appetizers, grilled, stuffed, marinated, preserved, or used in sauces. They come in all colors, shapes, and sizes. Take advantage and cultivate several varieties in your vegetable garden to enjoy a variety of flavors!
Harvesting: Harvest periods vary depending on the maturity: early varieties are harvested from 55 to 70 days after planting, mid-season varieties from 70 to 85 days, and late varieties beyond 85 days. The fruits should be picked when they reach their final color and show a slight softening while remaining firm. For better preservation, it is recommended to pick the fruit with its stem. Be careful, immature fruits, stems, and leaves contain solanine and should not be consumed.
Storage: The optimal storage temperature for tomatoes is between 10 and 15°C (50 and 59°F). Refrigeration is possible but alters the taste quality of the fruits. For longer storage, tomatoes can be preserved by confit, dried, frozen, canned, or cooked into jam. To confit them, cut your tomatoes in half and collect the juice. Place your half tomatoes facing up on a baking sheet. Season with salt, pepper, and sugar, then bake at a very low temperature for at least an hour. Remove the tomatoes, store them in a glass jar, and cover with olive oil.
Gardener's tip: To reduce the need for watering, it is recommended to mulch the soil with thin successive layers of grass clippings, preferably mixed with dead leaves. This protection helps the soil retain moisture and also reduces weed growth.
Tomato Grafted Cauralina F1 Tomato Plants in pictures


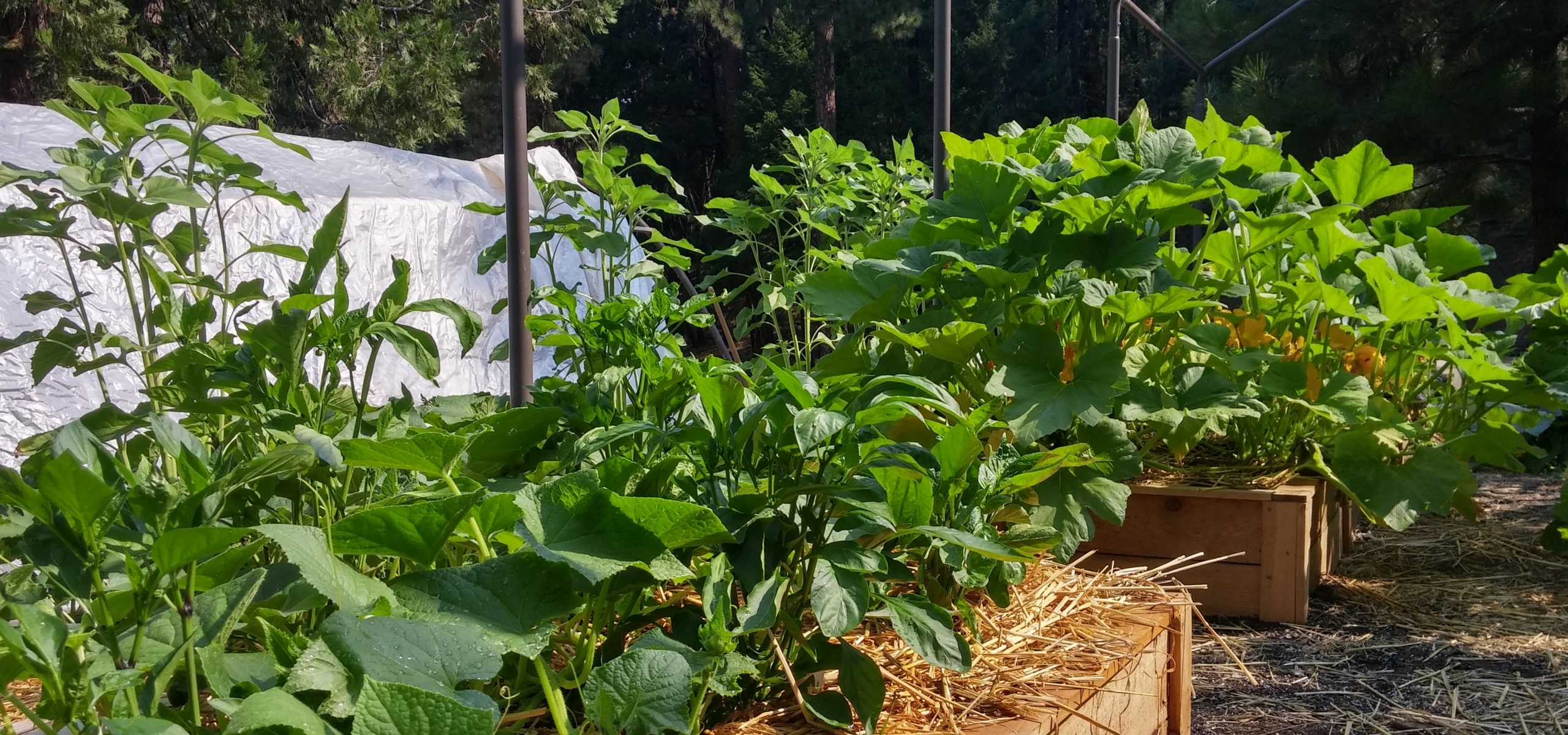
Harvest
Plant habit
Foliage
Planting and care
Tomato plants are easy to grow. Sunlight and heat are crucial for the success of this crop. Tomatoes thrive in rich, well-draining soil that has been deeply tilled. A few months before planting, add well-rotted compost after loosening the soil. If your soil is heavy, add some sand at the time of planting.
Initially, allow the plug plants to grow by transplanting them into 8 to 10.5 cm (3 to 4in) buckets filled with potting soil. Place them in a sunny and heated location, ensuring the temperature never drops below 12-14°C (53.6-57.2°F), as this can cause the foliage to turn yellow and stunt the plant's growth. Once the plants reach a height of approximately 15 cm (6in), transplant them into the ground if the outside temperatures allow.
Planting in the ground should be done once the risk of frost has passed, usually after the Ice Saints in mid-May. Choose a sunny and sheltered location. Space the plants 50 cm (20in) apart in rows and 70 cm (28in) between rows if pruning, or 1m (0 or 3ft) in all directions for unpruned cultivation. Dig a hole (3 times the volume of the plug plant), add some well-decomposed compost to the bottom of the hole. Place your plant, which can be buried up to the first leaves, then backfill. Firm the soil, create a basin around the base, and water generously. Be careful not to wet the leaves to protect your plants from fungal diseases.
Install stakes (soon after planting to avoid damaging the roots). Mulch around the base of the plants. Water regularly as irregular watering can lead to a calcium deficiency, resulting in blossom end rot.
In addition, tomatoes, like potatoes, are susceptible to late blight. This is a fungal disease caused by the Phytophthora infestans fungus. Late blight develops in warm and humid conditions. Small spots appear, white on the undersides of leaves and green-gray on top. To reduce the risks, space the plants adequately and avoid watering the foliage. In terms of crop rotation, wait 4 years before growing any Solanaceae plants in the same spot and avoid planting them in neighboring rows. If necessary, spray with Bordeaux mixture or prepare decoctions using horsetail or garlic.
Less common, tomato cultivation in pots is still possible by choosing varieties with small fruits and placing the pot in a sunny location.
Cultivation
Care
Intended location
Planting & care advice
This item has not been reviewed yet - be the first to leave a review about it.
Similar products
Haven't found what you were looking for?
Hardiness is the lowest winter temperature a plant can endure without suffering serious damage or even dying. However, hardiness is affected by location (a sheltered area, such as a patio), protection (winter cover) and soil type (hardiness is improved by well-drained soil).
Photo Sharing Terms & Conditions
In order to encourage gardeners to interact and share their experiences, Promesse de fleurs offers various media enabling content to be uploaded onto its Site - in particular via the ‘Photo sharing’ module.
The User agrees to refrain from:
- Posting any content that is illegal, prejudicial, insulting, racist, inciteful to hatred, revisionist, contrary to public decency, that infringes on privacy or on the privacy rights of third parties, in particular the publicity rights of persons and goods, intellectual property rights, or the right to privacy.
- Submitting content on behalf of a third party;
- Impersonate the identity of a third party and/or publish any personal information about a third party;
In general, the User undertakes to refrain from any unethical behaviour.
All Content (in particular text, comments, files, images, photos, videos, creative works, etc.), which may be subject to property or intellectual property rights, image or other private rights, shall remain the property of the User, subject to the limited rights granted by the terms of the licence granted by Promesse de fleurs as stated below. Users are at liberty to publish or not to publish such Content on the Site, notably via the ‘Photo Sharing’ facility, and accept that this Content shall be made public and freely accessible, notably on the Internet.
Users further acknowledge, undertake to have ,and guarantee that they hold all necessary rights and permissions to publish such material on the Site, in particular with regard to the legislation in force pertaining to any privacy, property, intellectual property, image, or contractual rights, or rights of any other nature. By publishing such Content on the Site, Users acknowledge accepting full liability as publishers of the Content within the meaning of the law, and grant Promesse de fleurs, free of charge, an inclusive, worldwide licence for the said Content for the entire duration of its publication, including all reproduction, representation, up/downloading, displaying, performing, transmission, and storage rights.
Users also grant permission for their name to be linked to the Content and accept that this link may not always be made available.
By engaging in posting material, Users consent to their Content becoming automatically accessible on the Internet, in particular on other sites and/or blogs and/or web pages of the Promesse de fleurs site, including in particular social pages and the Promesse de fleurs catalogue.
Users may secure the removal of entrusted content free of charge by issuing a simple request via our contact form.
The flowering period indicated on our website applies to countries and regions located in USDA zone 8 (France, the United Kingdom, Ireland, the Netherlands, etc.)
It will vary according to where you live:
- In zones 9 to 10 (Italy, Spain, Greece, etc.), flowering will occur about 2 to 4 weeks earlier.
- In zones 6 to 7 (Germany, Poland, Slovenia, and lower mountainous regions), flowering will be delayed by 2 to 3 weeks.
- In zone 5 (Central Europe, Scandinavia), blooming will be delayed by 3 to 5 weeks.
In temperate climates, pruning of spring-flowering shrubs (forsythia, spireas, etc.) should be done just after flowering.
Pruning of summer-flowering shrubs (Indian Lilac, Perovskia, etc.) can be done in winter or spring.
In cold regions as well as with frost-sensitive plants, avoid pruning too early when severe frosts may still occur.
The planting period indicated on our website applies to countries and regions located in USDA zone 8 (France, United Kingdom, Ireland, Netherlands).
It will vary according to where you live:
- In Mediterranean zones (Marseille, Madrid, Milan, etc.), autumn and winter are the best planting periods.
- In continental zones (Strasbourg, Munich, Vienna, etc.), delay planting by 2 to 3 weeks in spring and bring it forward by 2 to 4 weeks in autumn.
- In mountainous regions (the Alps, Pyrenees, Carpathians, etc.), it is best to plant in late spring (May-June) or late summer (August-September).
The harvesting period indicated on our website applies to countries and regions in USDA zone 8 (France, England, Ireland, the Netherlands).
In colder areas (Scandinavia, Poland, Austria...) fruit and vegetable harvests are likely to be delayed by 3-4 weeks.
In warmer areas (Italy, Spain, Greece, etc.), harvesting will probably take place earlier, depending on weather conditions.
The sowing periods indicated on our website apply to countries and regions within USDA Zone 8 (France, UK, Ireland, Netherlands).
In colder areas (Scandinavia, Poland, Austria...), delay any outdoor sowing by 3-4 weeks, or sow under glass.
In warmer climes (Italy, Spain, Greece, etc.), bring outdoor sowing forward by a few weeks.














































