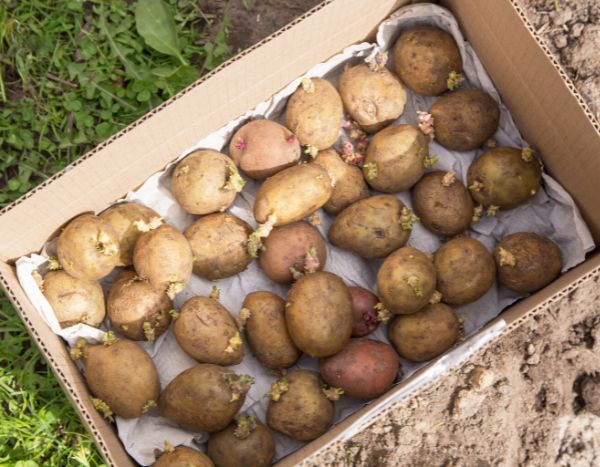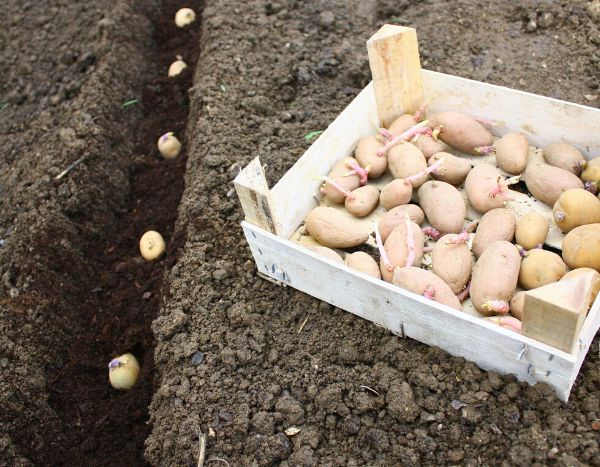

Pommes de terre Ulysse en plants - Solanum tuberosum
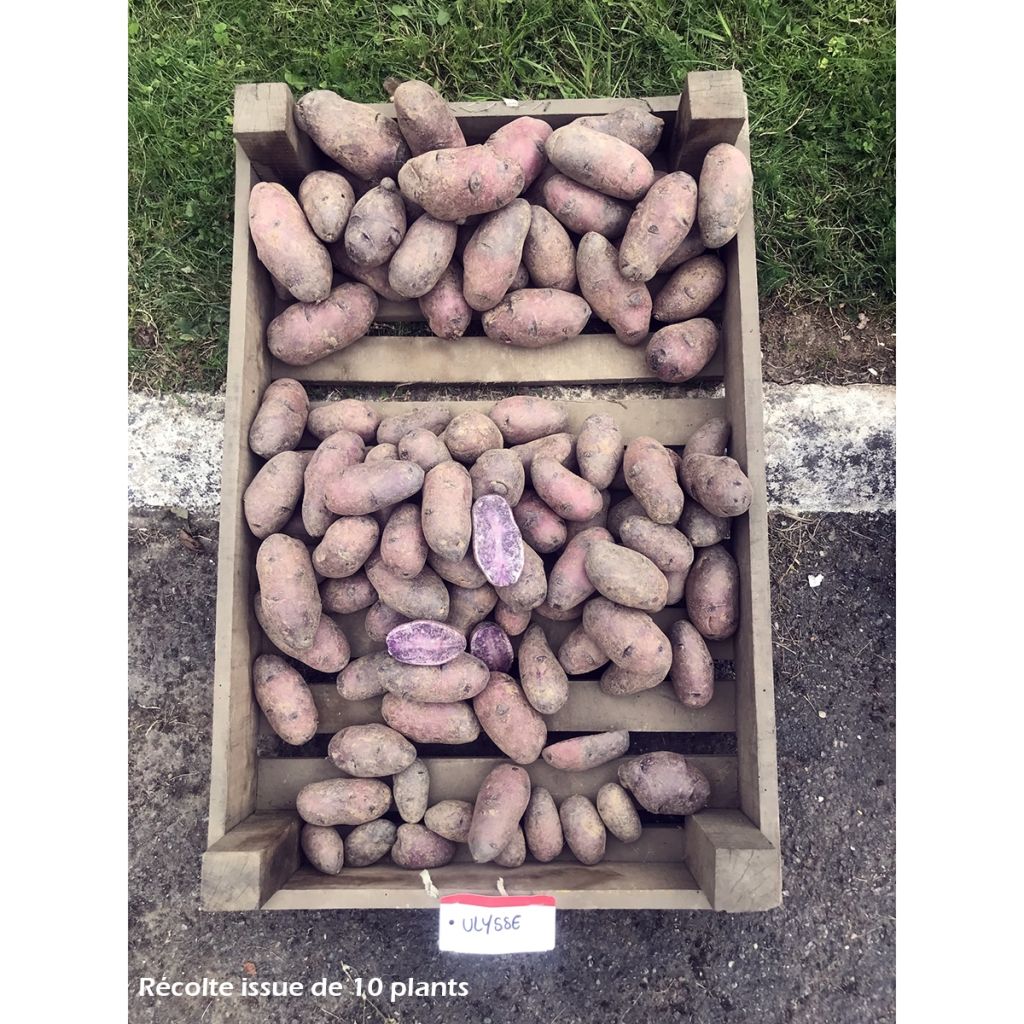


Pommes de terre Ulysse - Solanum tuberosum
Potatoes Ulysse
Solanum tuberosum Ulysse
Potato
Complete disappointment with one of the products delivered. Several rotten potatoes and others are soft in the bag.
Serge, 13/03/2021
Special offer!
Receive a €20 voucher for any order over €90 (excluding delivery costs, credit notes, and plastic-free options)!
1- Add your favorite plants to your cart.
2- Once you have reached €90, confirm your order (you can even choose the delivery date!).
3- As soon as your order is shipped, you will receive an email containing your voucher code, valid for 3 months (90 days).
Your voucher is unique and can only be used once, for any order with a minimum value of €20, excluding delivery costs.
Can be combined with other current offers, non-divisible and non-refundable.
Home or relay delivery (depending on size and destination)
Schedule delivery date,
and select date in basket
This plant carries a 6 months recovery warranty
More information
We guarantee the quality of our plants for a full growing cycle, and will replace at our expense any plant that fails to recover under normal climatic and planting conditions.
Description
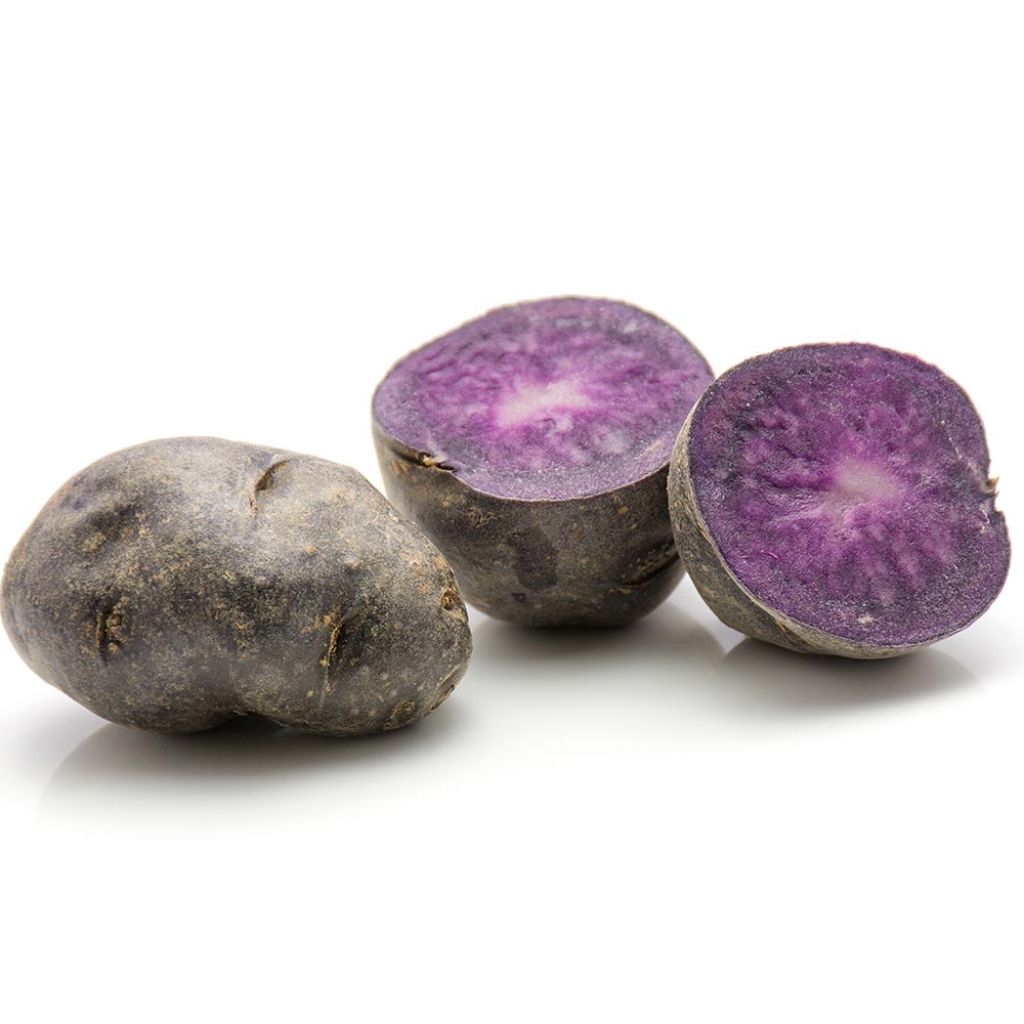
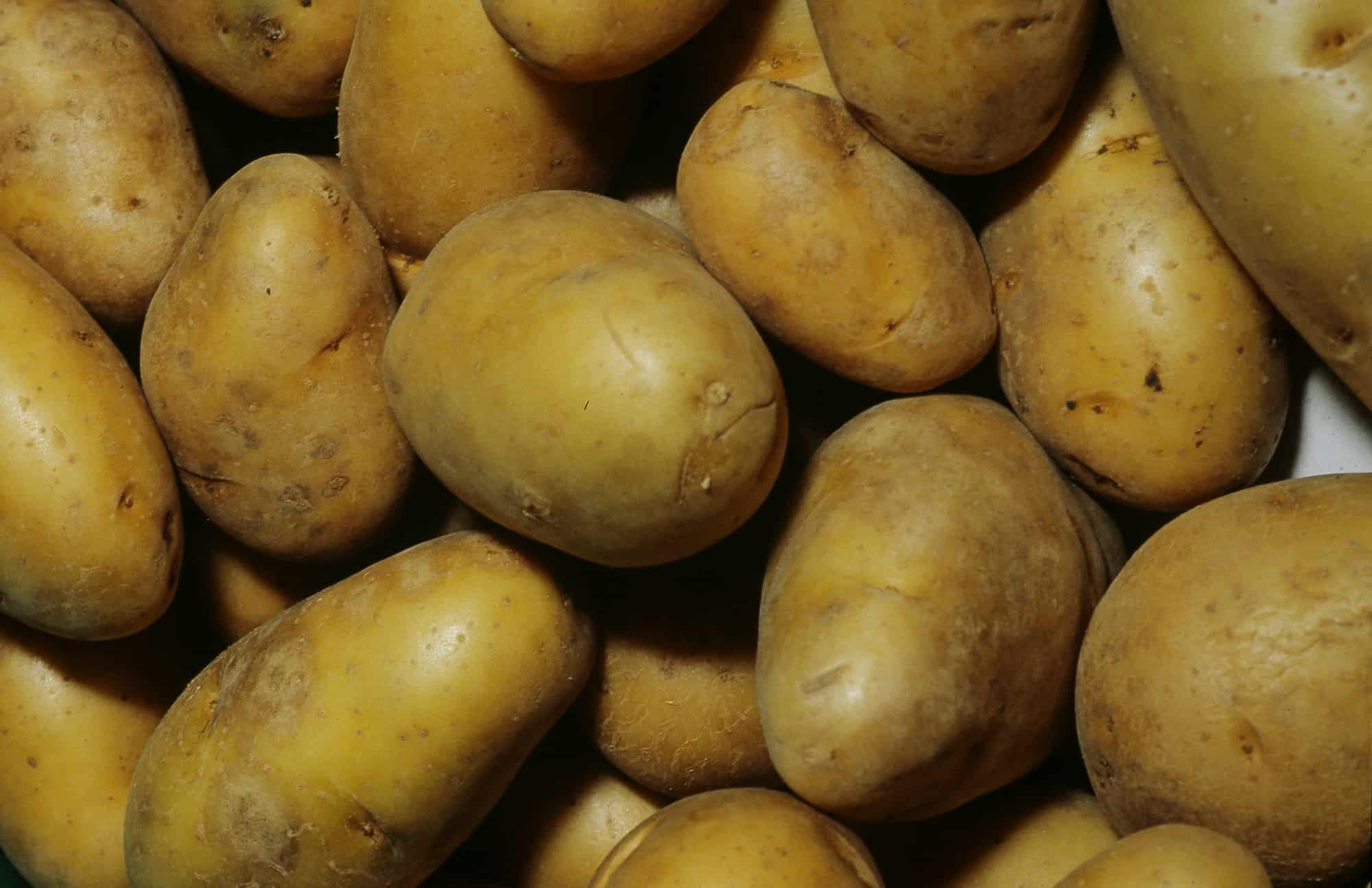
The 'Ulysse' potato is a new original French selection, derived from two proven varieties: Ditta and Bleue d'artois. It produces oval and regular tubers with a beautiful slate blue-violet skin and flesh. In the garden, it is a mid-late variety that is easy to grow, offering a good yield of medium-sized potatoes and is resistant to blight. It can be stored for a long time in a cool and dark place. In terms of cooking, it is versatile, and its firm flesh marbled with white has a surprising flavor. Try thinly sliced as chips, mashed, or steamed. It can be planted from March to May for a harvest approximately 120 days later, from June to August. Certified plants. Size: 28/40 mm (1/2in).
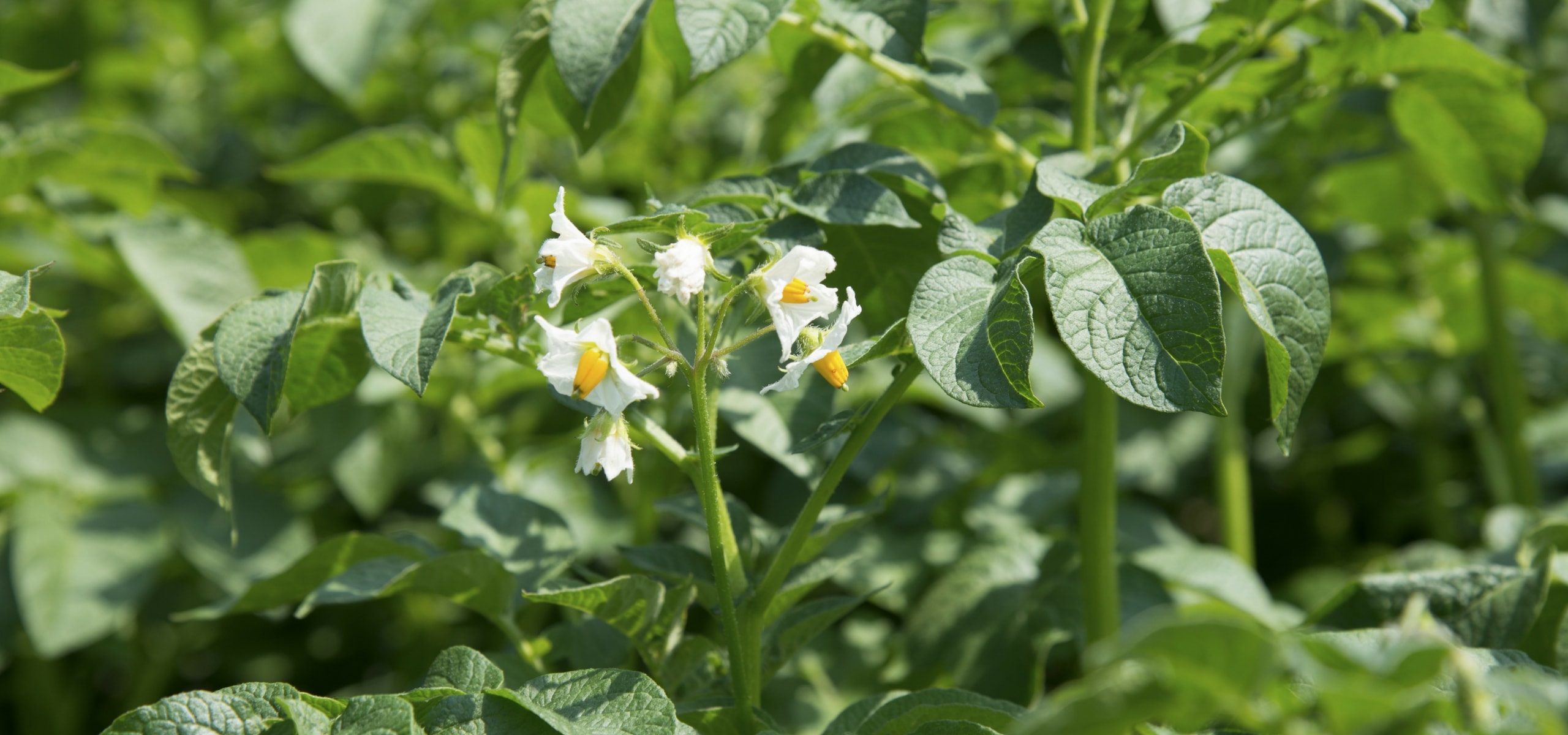
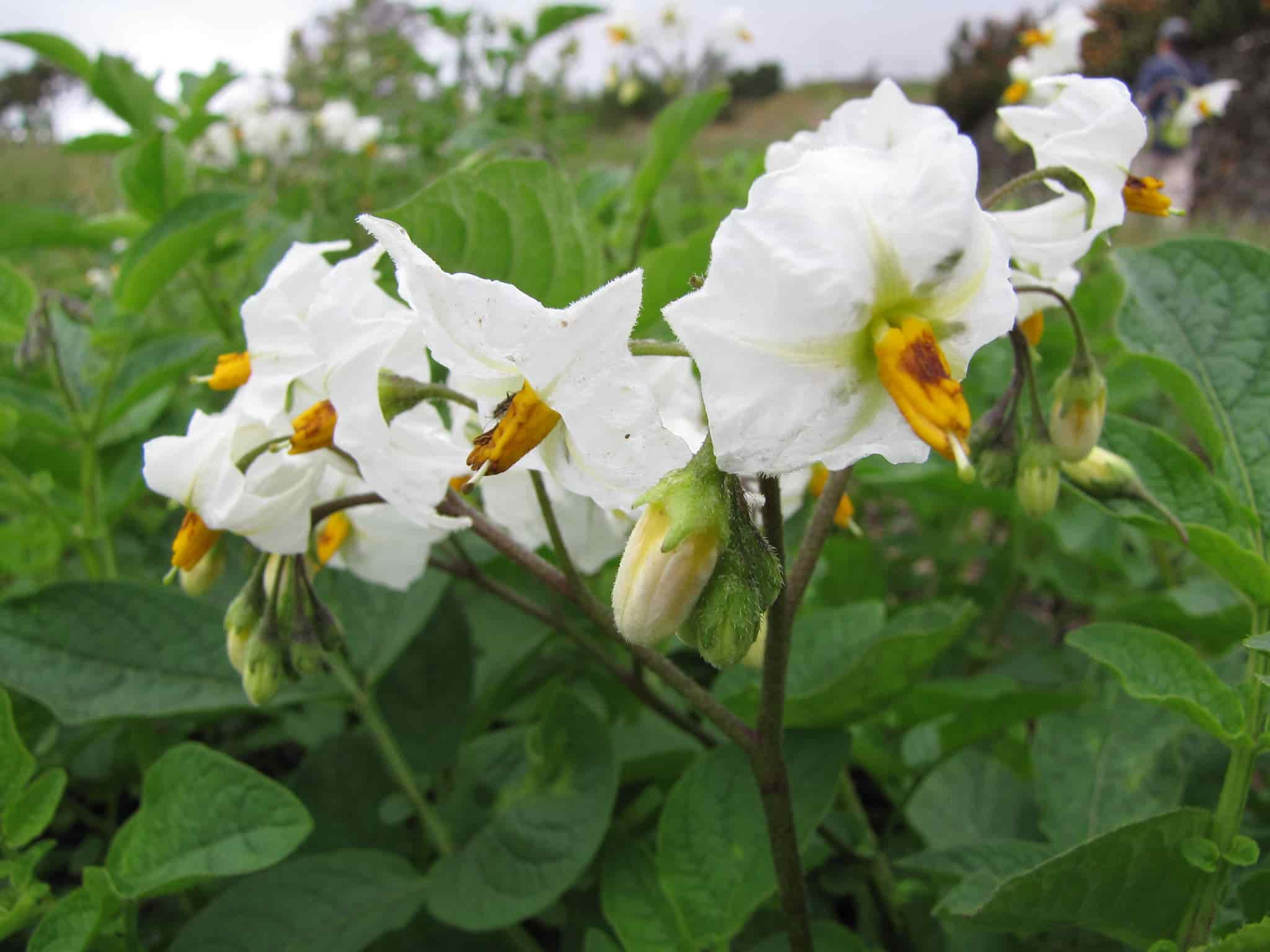
Potato is a root vegetable that has become essential in both the vegetable garden and the kitchen. It is a perennial plant cultivated as an annual, developing tubers as reserve organs on its rhizomes. Except for a few varieties like Belle de Fontenay, the plants produce small flowers in the summer. Each plant will produce several potatoes, which can be stored for several months and cooked in multiple ways. Potatoes belong to the Solanaceae family, like eggplants and tomatoes. Originally cultivated in the Andes Mountains, it was brought to Europe in the 16th century. It was only around 1750 that it became widely developed in France, thanks to Parmentier.
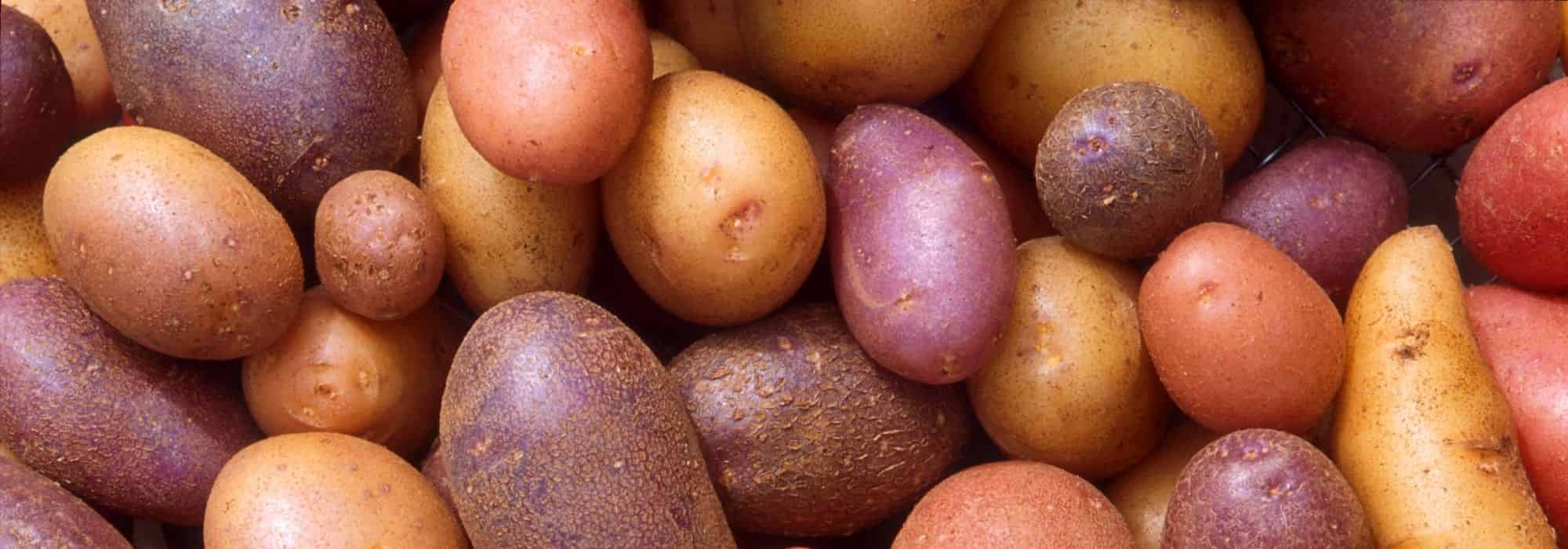
There are many varieties available. The tubers, which can be more or less elongated, have flesh that is generally yellow, sometimes red, pink, or purple. Low in calories, potatoes are rich in carbohydrates, iron, and potassium.
There are three categories of potatoes, based on the flesh content:
- Firm-fleshed varieties have good cooking properties. These rather elongated potatoes have fine and tasty flesh. They are ideal for boiling or steaming and can also be stewed or fried.
- Floury-fleshed varieties are rich in starch and easily mashable. Fairly large, these potatoes are perfect for making mashed potatoes or soups. They also make very crispy fries as they tend to absorb less oil when cooked.
- Waxy-fleshed varieties have a melting texture while maintaining good cooking properties. They can be used in various ways: fried, stewed, or baked.
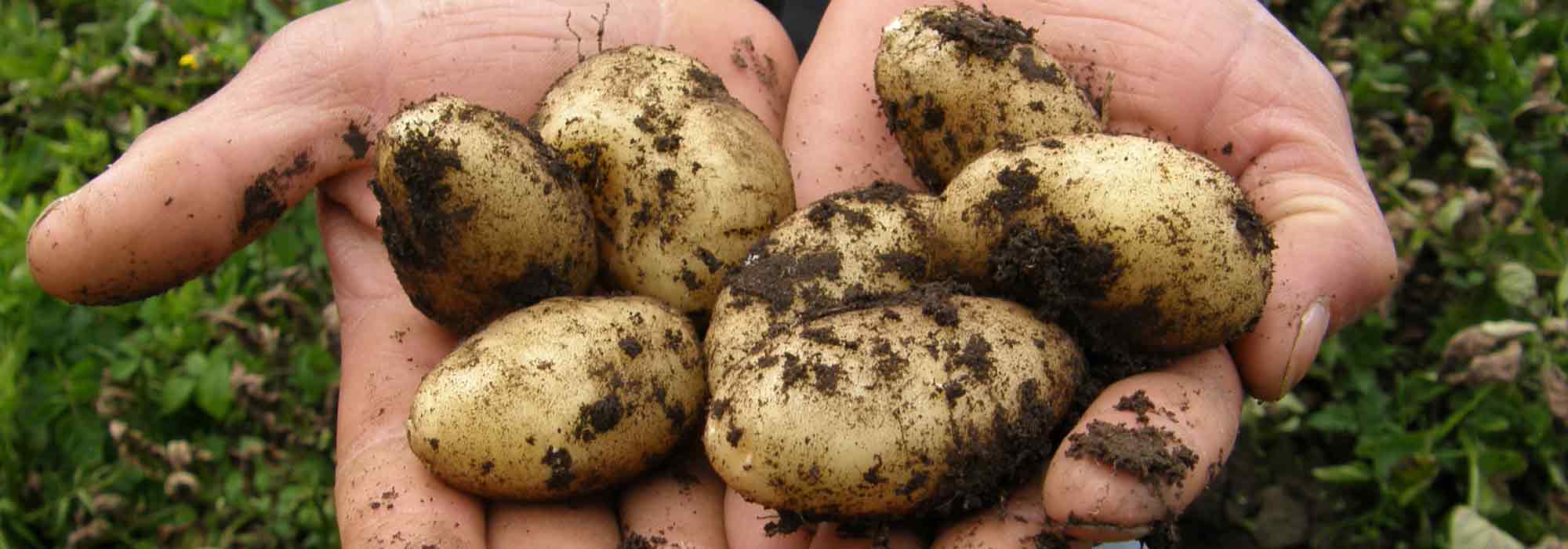
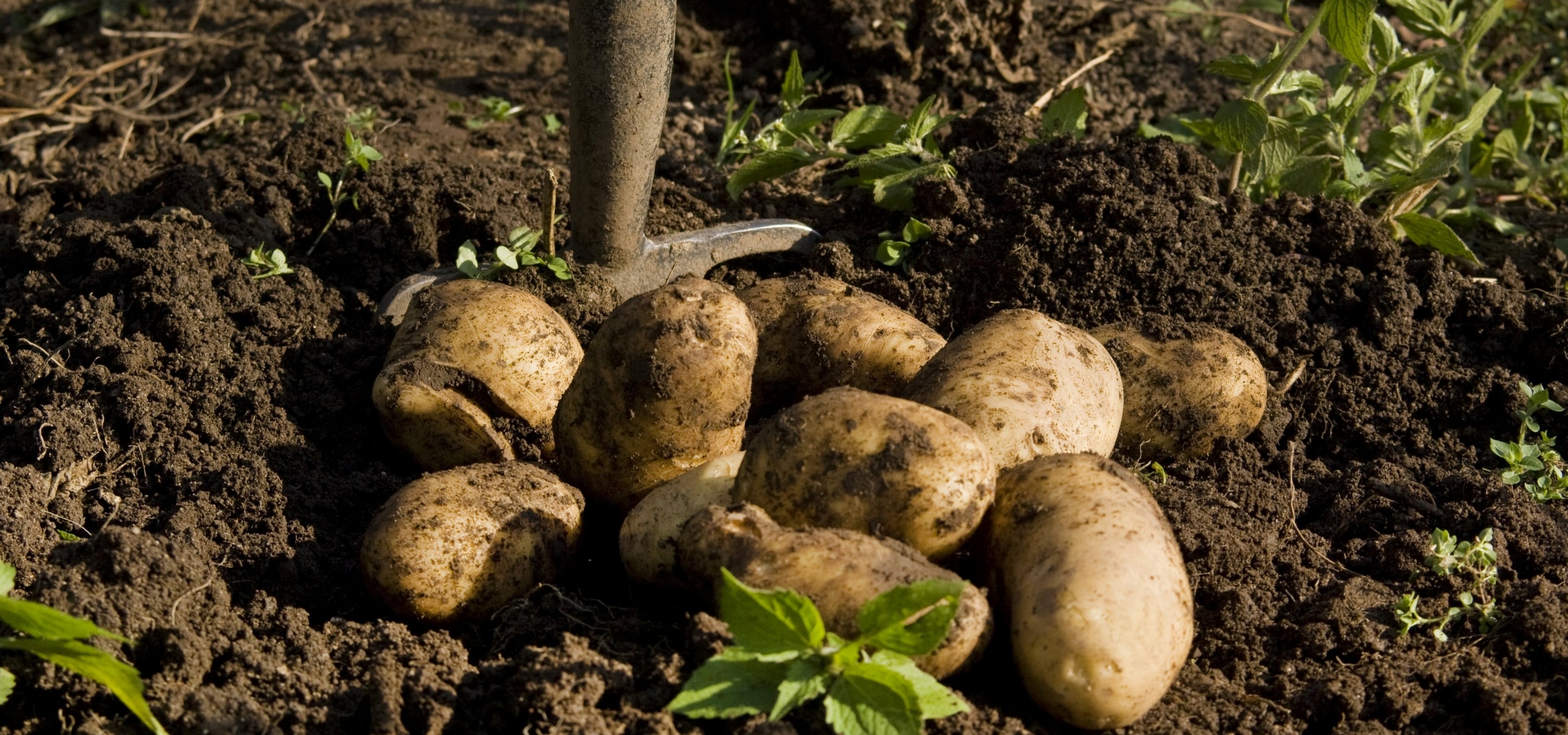
Harvesting: Depending on the variety and their earliness, potatoes can be harvested from May to October. Gently lift the plants with a garden fork to avoid damaging the tubers. Let the potatoes dry in the sun for a day.
Storage potatoes should be harvested when the foliage turns yellow and withers. Early varieties are harvested 80 to 90 days after planting, mid-early varieties around 110 days, mid-late varieties around 120 days, and late varieties from 120 to over 150 days.
As for new potatoes, with their very thin skin and delicious flesh, they are harvested before maturity, 70 days after planting. Harvest them just after flowering, around May-June.
Storage: After removing any damaged tubers, store potatoes in a cool, dry, and dark place. In the presence of light, potatoes turn green and produce a toxic compound called solanine. Early-harvested varieties should be consumed quickly. Storage potatoes can be stored for several months. The duration of storage varies depending on their earliness: late varieties have the longest storage life.
Gardener's tip: Grow potatoes in a crop rotation system as they are often considered a cleansing crop. The hilling and root development leave the soil clean and loose after harvest. They also benefit from the proximity of legumes such as beans, broad beans, and peas.
Harvest
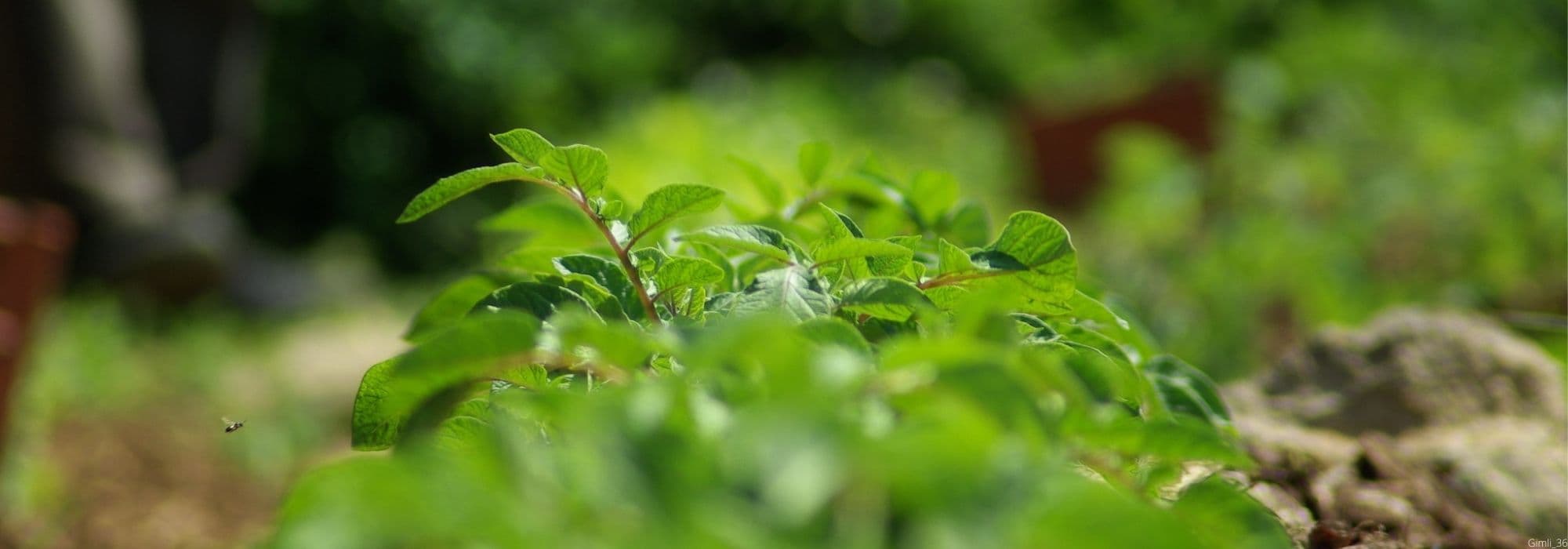
Plant habit
Foliage
Planting and care
Planting: Potatoes need a light, deep, and rich soil. Choose a sunny location. Add well-rotted compost in the previous autumn by scratching it into the soil after loosening it. Planting takes place under cover in February-March for early-harvest varieties. For other varieties, plant them from mid-March to May depending on the climate. Wait until the soil temperature is at least 10°C (50°F). The flowering of the lilac is often a landmark for starting the planting. Install several varieties in your vegetable garden to vary the pleasures!
Loosen the soil deeply and form rows 10 cm (4in) deep, spaced 70 cm (28in) apart. Place the tubers, sprout upwards, every 40 cm (16in) (or 30 cm (12in) for early-harvest varieties). Cover with fine soil. When the plants reach 15 cm (6in), hill up by bringing fine soil to the base of the stems, up to 20 cm (8in) in height. Hilling up will promote tuber formation and water drainage. You can hill them up again a month later. Mulch at the base of the plants with thin successive layers of grass clippings mixed with dead leaves if possible. This protection, which keeps the soil moist, also limits weed growth.
Potato cultivation does not require watering, except in case of extreme heat. In this case, water the base of the plant without wetting the foliage to prevent the occurrence of fungal diseases.
Diseases and pests: Potatoes are susceptible, just like tomatoes, to late blight. This is a fungal disease caused by the Phytophthora infestans fungus. Late blight develops in warm and humid weather. Small spots appear, white on the underside of the leaves and brown on top. As a preventive measure, here are some tips to reduce the risk of late blight:
-
Do not grow several plants from the Solanaceae family (potatoes, tomatoes, eggplants, peppers, chili peppers, etc.) in neighboring rows, as they are susceptible to the same diseases.
-
In terms of crop rotation, wait 4 years before growing another Solanaceae plant in the same location.
-
Space the plants, both within and between rows, to promote air circulation and prevent rapid disease spread.
-
If you need to water, avoid wetting the foliage.
-
Spray with Bordeaux mixture or preparations such as horsetail decoction or garlic purée.
Harvest can also be disrupted by the Colorado potato beetle, a beetle of the order Coleoptera. You will recognize it by its yellow head and its yellow and black striped body. The best solution, although a bit time-consuming, is to remove them as they appear. As a preventive measure, sow blue flax seeds between your rows of potatoes. Sow from April to June in shallow furrows. Besides being repellent to Colorado potato beetles, flax will brighten up your vegetable garden with its pretty little blue flowers. You can also interplant peas between your rows of potatoes.
Other planting methods: The detailed planting method above is the most common. Other methods exist, such as mulch planting and tower planting.
Mulch planting involves placing the tubers on the ground and covering them with a layer of mulch. This protection is gradually increased as the plant grows, ensuring that the tubers are always shielded from light.
Tower planting or bag planting is practical for small spaces but requires regular watering. The tower can be constructed from various materials (wood, wire mesh, bag, tires, etc). The tubers are placed on a bed of potting soil or compost. As the plant grows, it is covered with more potting soil, leaving only the topmost leaves exposed, and so on until the top of the tower, allowing the tubers to form throughout the height of the container. Harvest when the foliage has withered.
Cultivation
Care
Intended location
Planting & care advice
-
, onOrder confirmed
Reply from on Promesse de fleurs
Similar products
Haven't found what you were looking for?
Hardiness is the lowest winter temperature a plant can endure without suffering serious damage or even dying. However, hardiness is affected by location (a sheltered area, such as a patio), protection (winter cover) and soil type (hardiness is improved by well-drained soil).
Photo Sharing Terms & Conditions
In order to encourage gardeners to interact and share their experiences, Promesse de fleurs offers various media enabling content to be uploaded onto its Site - in particular via the ‘Photo sharing’ module.
The User agrees to refrain from:
- Posting any content that is illegal, prejudicial, insulting, racist, inciteful to hatred, revisionist, contrary to public decency, that infringes on privacy or on the privacy rights of third parties, in particular the publicity rights of persons and goods, intellectual property rights, or the right to privacy.
- Submitting content on behalf of a third party;
- Impersonate the identity of a third party and/or publish any personal information about a third party;
In general, the User undertakes to refrain from any unethical behaviour.
All Content (in particular text, comments, files, images, photos, videos, creative works, etc.), which may be subject to property or intellectual property rights, image or other private rights, shall remain the property of the User, subject to the limited rights granted by the terms of the licence granted by Promesse de fleurs as stated below. Users are at liberty to publish or not to publish such Content on the Site, notably via the ‘Photo Sharing’ facility, and accept that this Content shall be made public and freely accessible, notably on the Internet.
Users further acknowledge, undertake to have ,and guarantee that they hold all necessary rights and permissions to publish such material on the Site, in particular with regard to the legislation in force pertaining to any privacy, property, intellectual property, image, or contractual rights, or rights of any other nature. By publishing such Content on the Site, Users acknowledge accepting full liability as publishers of the Content within the meaning of the law, and grant Promesse de fleurs, free of charge, an inclusive, worldwide licence for the said Content for the entire duration of its publication, including all reproduction, representation, up/downloading, displaying, performing, transmission, and storage rights.
Users also grant permission for their name to be linked to the Content and accept that this link may not always be made available.
By engaging in posting material, Users consent to their Content becoming automatically accessible on the Internet, in particular on other sites and/or blogs and/or web pages of the Promesse de fleurs site, including in particular social pages and the Promesse de fleurs catalogue.
Users may secure the removal of entrusted content free of charge by issuing a simple request via our contact form.
The flowering period indicated on our website applies to countries and regions located in USDA zone 8 (France, the United Kingdom, Ireland, the Netherlands, etc.)
It will vary according to where you live:
- In zones 9 to 10 (Italy, Spain, Greece, etc.), flowering will occur about 2 to 4 weeks earlier.
- In zones 6 to 7 (Germany, Poland, Slovenia, and lower mountainous regions), flowering will be delayed by 2 to 3 weeks.
- In zone 5 (Central Europe, Scandinavia), blooming will be delayed by 3 to 5 weeks.
In temperate climates, pruning of spring-flowering shrubs (forsythia, spireas, etc.) should be done just after flowering.
Pruning of summer-flowering shrubs (Indian Lilac, Perovskia, etc.) can be done in winter or spring.
In cold regions as well as with frost-sensitive plants, avoid pruning too early when severe frosts may still occur.
The planting period indicated on our website applies to countries and regions located in USDA zone 8 (France, United Kingdom, Ireland, Netherlands).
It will vary according to where you live:
- In Mediterranean zones (Marseille, Madrid, Milan, etc.), autumn and winter are the best planting periods.
- In continental zones (Strasbourg, Munich, Vienna, etc.), delay planting by 2 to 3 weeks in spring and bring it forward by 2 to 4 weeks in autumn.
- In mountainous regions (the Alps, Pyrenees, Carpathians, etc.), it is best to plant in late spring (May-June) or late summer (August-September).
The harvesting period indicated on our website applies to countries and regions in USDA zone 8 (France, England, Ireland, the Netherlands).
In colder areas (Scandinavia, Poland, Austria...) fruit and vegetable harvests are likely to be delayed by 3-4 weeks.
In warmer areas (Italy, Spain, Greece, etc.), harvesting will probably take place earlier, depending on weather conditions.
The sowing periods indicated on our website apply to countries and regions within USDA Zone 8 (France, UK, Ireland, Netherlands).
In colder areas (Scandinavia, Poland, Austria...), delay any outdoor sowing by 3-4 weeks, or sow under glass.
In warmer climes (Italy, Spain, Greece, etc.), bring outdoor sowing forward by a few weeks.


















































