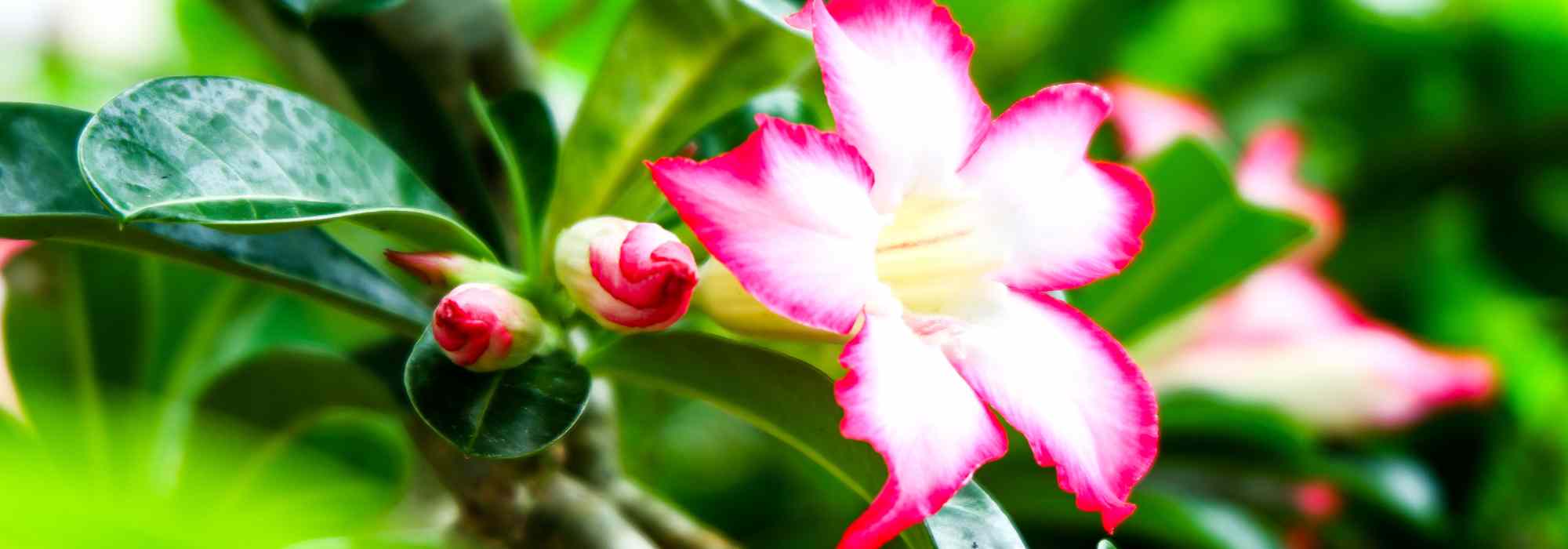

Adenium - Desert rose : how to grow and care for it
Contents
The Adenium in a nutshell
- The Adenium obesum, or Desert Rose, is a succulent plant.
- It boasts a very graphic appearance thanks to its swollen caudex.
- In summer, beautiful pink, red, or white funnel-shaped flowers cover the foliage.
- It thrives in full sun and requires a very well-draining soil to avoid rot.
- It’s the perfect plant for a minimalist, exotic, or modern decor.
The word from our expert
The Adenium obesum, better known as the Desert Rose, is an incredible plant belonging to the Apocynaceae family. Native to the arid regions of East Africa and the Arabian Peninsula, it stands out for its swollen caudex, which allows it to store water and survive long periods of drought. Its sculptural habit, combined with striking flowering in shades of pink, red, or white, makes it a true work of botanical art, highly prized by collectors and enthusiasts of exotic plants.
Easy to grow in pots, the Adenium requires a very well-draining substrate, a terracotta pot, and full sun exposure to thrive. Its watering needs to be carefully managed: regular in summer, almost non-existent in winter, to avoid any risk of rot. During the growth period, a balanced fertiliser encourages generous flowering, while occasional pruning helps shape its silhouette and promote branching.
Although hardy, the Desert Rose can be susceptible to mealybugs, spider mites, and excess moisture, which encourage root rot. Regular monitoring and good growing conditions are usually enough to prevent these issues.
In terms of decoration, the Adenium fits perfectly into a modern, bohemian, or exotic interior, enhanced by a matte ceramic, concrete, or terracotta pot. Its unique appearance makes it a centrepiece in a succulent collection or an open desert-style terrarium. A true botanical gem, this exceptional plant captivates as much for its resilience as for its rare elegance.
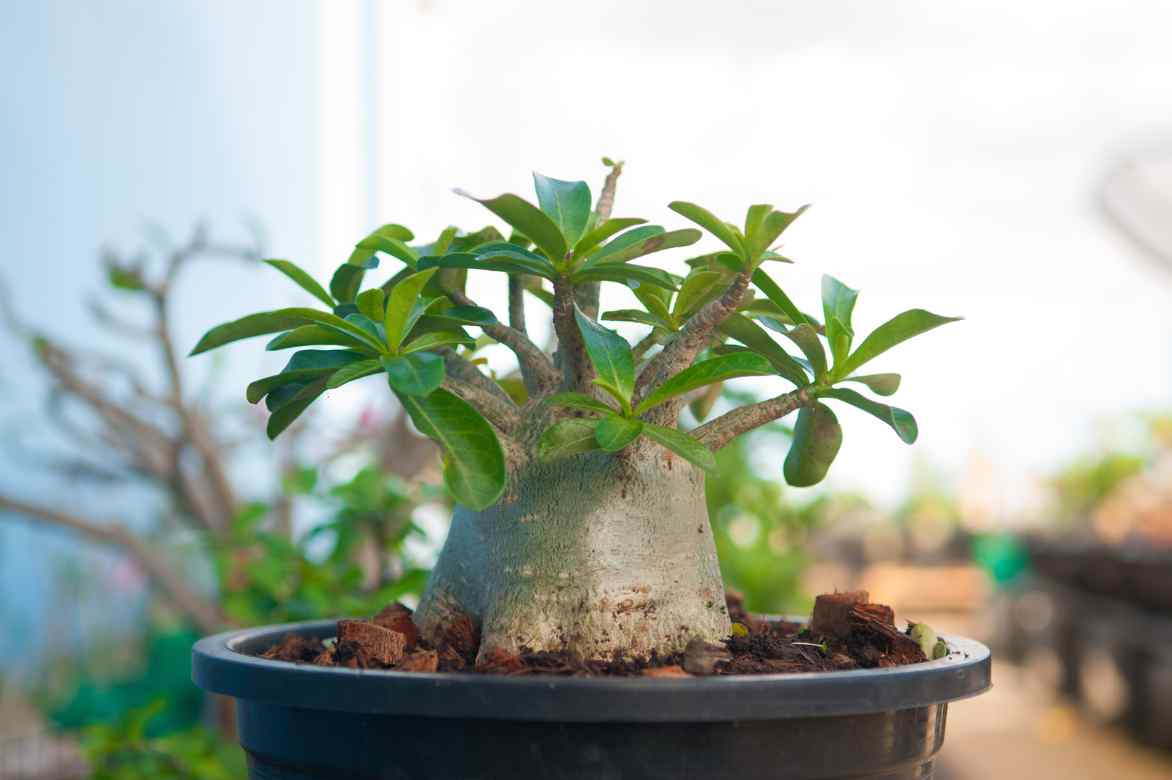

Adenium obesum
Botany and description
Botanical data
- Latin name Adenium obesum
- Family Apocynaceae
- Common name Desert Rose
- Flowering May to September
- Height in pot, 50 cm
- Sun exposure sun
- Soil type light and well-draining substrate
- Hardiness 5°C
The Adenium belongs to the Apocynaceae family, a large botanical family that includes often exotic, sometimes toxic, but always fascinating plants. Its genus name, Adenium, originates from the ancient region of Aden in Yemen, where one of the first species was described. In French, it is commonly called “Desert Rose”, an evocative name that reflects both the beauty of its flowers and its incredible ability to survive in arid environments.
In its natural habitat, the Adenium grows in dry and sunny areas, whether in East Africa or the Arabian Peninsula. It is distinguished by its swollen trunk, called a caudex, which allows it to store water and withstand long periods of drought. This sculptural aspect, combined with its vibrant flowers in shades of pink, red, or white, makes it a highly sought-after houseplant. Its relatively simple care, slow growth, and elegant appearance appeal to both succulent enthusiasts and bonsai lovers.
The most commonly cultivated species is Adenium obesum, with its massive caudex and vibrant flowers that somewhat resemble those of the frangipani. However, hybrids derived from Adenium arabicum, with an even thicker trunk, are also occasionally found.
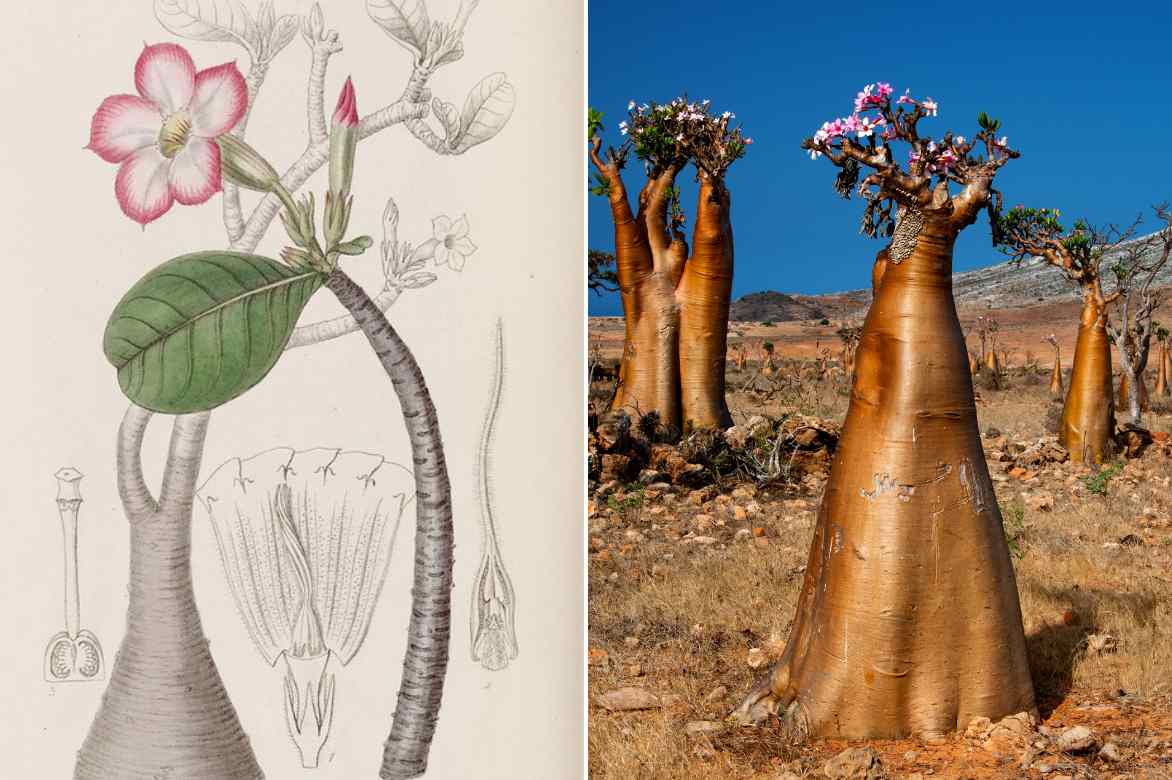
Adenium obesum botanical plate circa 1829, and Adenium obesum socotranum in its natural habitat
The Desert Rose is a succulent or fleshy plant with a compact, often twisted habit, evoking the silhouette of a natural bonsai. Its root system is deep and fleshy, allowing it to store water and survive long periods of drought. Its trunk, thickened at the base, forms a spectacular caudex, swollen and irregular, giving it a unique sculptural appearance. From this trunk emerge relatively short, usually twisted branches, covered with green, smooth, and slightly thick leaves, which can be evergreen or deciduous depending on growing conditions.
Flowering is one of its main attractions, with funnel-shaped flowers in vibrant colours, ranging from pale pink to deep red, sometimes edged with white. The flower of Adenium obesum is described as infundibuliform (funnel-shaped) and is typical of the Apocynaceae family. It consists of five petals, slightly undulate, arranged in a star around an elongated floral tube. The floral tube, often lighter than the petals, houses the stamens fused to the corolla, another distinctive feature of the Apocynaceae. The pistil is discreet, nestled at the heart of the flower, facilitating pollination by foraging insects such as bees and butterflies.
In favourable climates, it can produce elongated fruits resembling small pods, which release lightweight seeds topped with a fine silky down once they reach maturity.

Adenium obesum
Cultivating an Adenium: Pot and Substrate
When to Plant an Adenium in a Pot?
The best time to plant an Adenium in a pot is in spring, when the plant resumes its growth after the winter dormancy period.
Choosing the Pot
The Adenium should be placed in an unglazed terracotta pot, which promotes good evaporation of moisture and reduces the risk of root rot. The size of the pot should match the caudex: it should not be too deep, as this could retain too much water, but wide enough to allow proper root development. Bonsai pots are perfect for this type of plant.

Choosing the Substrate
A very well-draining substrate is essential. An ideal mix includes:
- 50% light potting soil,
- 30% coarse sand,
- 20% pumice or perlite to improve drainage.
However, there are ready-to-use potting mixes, perfect for desert roses, such as cacti and succulent potting mixes.
Exposure
The Adenium needs intense light to thrive and flower. It should be placed in full sun, near a well-exposed window or outdoors once temperatures exceed 15°C. Indoors, a south or west-facing exposure is preferable.
Humidity and Ambient Temperature
The Adenium prefers dry air and does not tolerate excessive humidity. Avoid placing it in humid rooms, such as bathrooms or kitchens.
The Desert Rose loves warmth and dislikes the cold. Its ideal growth temperature ranges between 20 and 35°C, with a preference for warm, sunny days. Below 10°C, its growth slows down, and it enters dormancy. In winter, it is crucial to keep it at a minimum temperature of 12 to 15°C to avoid frost or root rot. If temperatures drop too low, the plant should be brought indoors to a bright, dry spot. The plant dies below 5°C.
Steps for Planting in a Pot
- Choose a pot with drainage holes at the bottom to ensure good drainage.
- Place a layer of gravel or clay pebbles at the bottom to prevent water stagnation.
- Fill the pot with the well-draining substrate, leaving a hollow to accommodate the plant.
- Position the Adenium, ensuring the base of the caudex is slightly above the substrate to avoid excess moisture.
- Top up with substrate without compacting too much, then leave the plant unwatered for a few days to allow the roots to heal before gradually resuming irrigation.
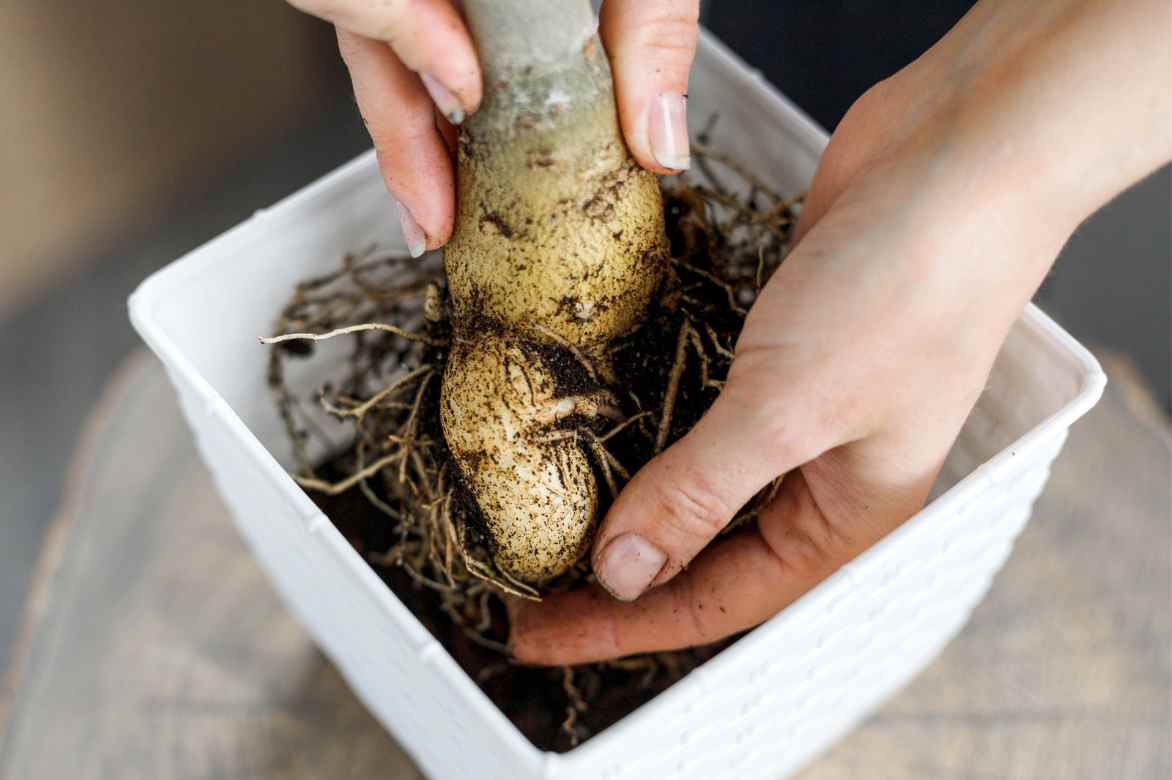

Repotting
Repotting should be done every two to three years, always in spring. On this occasion, it is recommended to replace the entire substrate to ensure good root aeration. You can slightly expose the thickened roots to highlight the caudex, but be careful not to bury the base of the trunk. After repotting, a temporary halt to watering is necessary to avoid the risk of rot and allow the roots to heal properly.
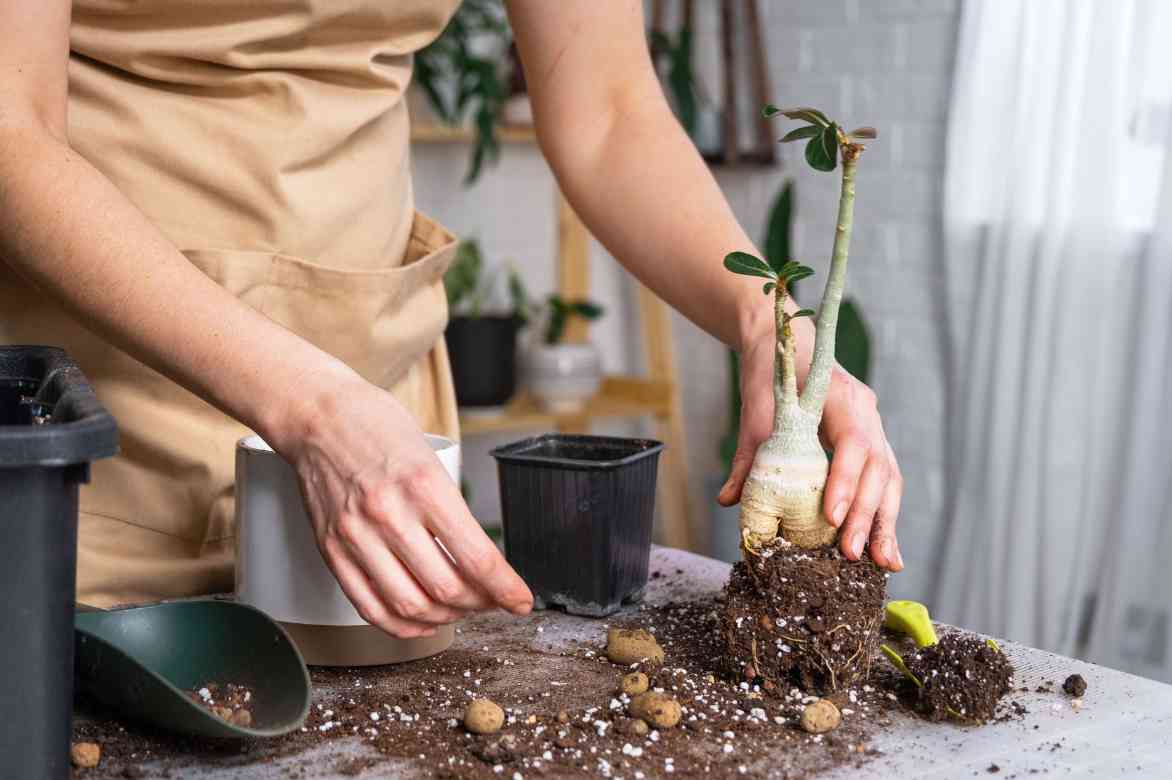

Culture and Care of an Adenium
Watering
When the Adenium is in full growth and flowering (spring-summer), water generously, but allow the substrate to dry out completely between waterings. On average, this means watering every 7 to 10 days in summer, depending on the heat and exposure.
In winter, when the plant is dormant, it is advisable to reduce watering, or even stop it for a few weeks, and avoid overly humid conditions, especially if the temperature is cool. A light monthly watering can be given if the plant is kept in a warm and dry environment.
Fertilisation
To encourage healthy growth and abundant flowering, the Adenium benefits from a balanced fertiliser. During spring and summer, a liquid fertiliser for flowering plants or cacti, rich in phosphorus and potassium, is recommended every 3 to 4 weeks. In autumn and winter, fertilising is unnecessary as the plant slows its activity.
Pruning and shaping
Pruning is not obligatory, but it helps to stimulate branching and achieve a more balanced habit. It should be done in early spring, before growth resumes. Overlong or unbalanced branches can be shortened to encourage a more compact structure. Pinching young shoots can also promote the development of new branches. After pruning, it is important to let the wounds dry before watering to avoid infection.
Precautions
The Adenium is a toxic plant, particularly its sap, which contains alkaloids that can irritate the skin and mucous membranes. It is therefore recommended to wear gloves when pruning and to wash your hands after handling. It should also be kept out of reach of children and pets.
→ Also check out our full article: “Adenium or Desert Rose: Care Through the Seasons“.
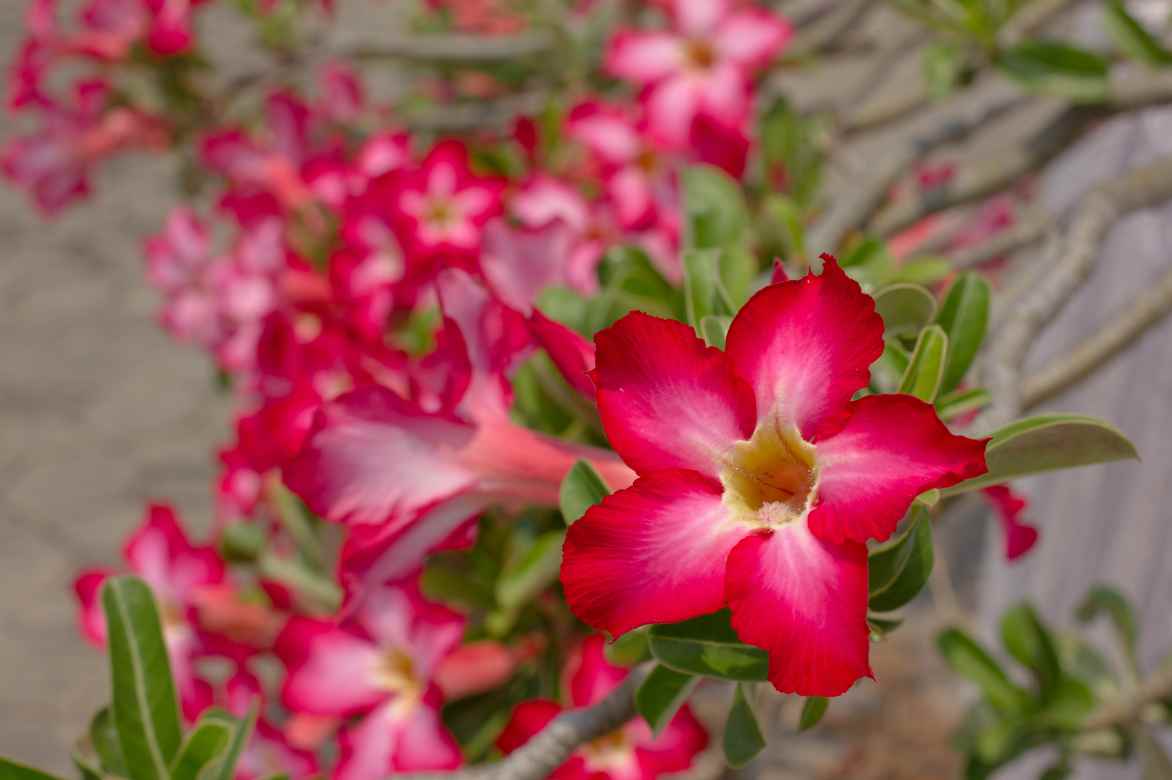

Fertilisation will help ensure beautiful flowering
Potential parasitic and disease issues
The Most Common Parasites
- Scale insects: these small white or brown parasites settle on the stems, under the leaves, and sometimes on the caudex, feeding on the sap and weakening the plant. They often leave a sticky residue (honeydew) that encourages the appearance of sooty mould (a black fungus). They can be removed with a cotton pad soaked in 70° alcohol.
- Red spider mites: these tiny mites appear in warm, dry conditions, causing yellowing of the leaves and the formation of fine webs. Increasing ambient humidity (not too much, as the desert rose dislikes it) and treatment with black soap can eradicate them.
- Aphids: less common, they may appear on young shoots in spring, weakening the plant. A simple jet of water or a spray of black soap is usually enough to eliminate them.
- Thrips: these tiny insects suck the sap from the leaves and flower buds, causing deformations and a silvery appearance on the foliage. Treatment with vegetable oil or a natural insecticide can help get rid of them.
Common Diseases
- Root and caudex rot: this is the most serious problem for Adenium, caused by overwatering or poorly drained soil. The caudex becomes soft and spongy, and the plant can quickly deteriorate. If the rot is localised, it is possible to cut away the affected parts with a sterilised tool, sprinkle with charcoal or cinnamon powder, and let it dry for a few days before replanting in dry soil.
- Stem rot: often due to excessive humidity, it manifests as black or brown spots that gradually spread. Pruning the affected parts and a fungicidal treatment can limit the damage.
- Sooty mould: this black fungus develops on the honeydew left by scale insects or aphids, covering the leaves with a dark layer that blocks photosynthesis. It disappears once the parasites are eliminated, by cleaning the leaves with soapy water.
How to Prevent These Problems?
- Avoid overwatering and always let the soil dry out between waterings.
- Ensure good ventilation by avoiding overly humid and confined atmospheres.
- Place the Adenium in full sunlight, as strong light strengthens its natural defences.
- Inspect the plant regularly to detect parasites as soon as they appear and intervene quickly with natural treatments.
To learn more about diseases and parasites of the desert rose, read our full article: Desert Rose, Adenium: Diseases and Parasites.
How to propagate an Adenium?
Adenium can be propagated by sowing and propagation by cuttings, each of these methods having its advantages and disadvantages.
Sowing (the preferred method for a beautiful caudex)
Propagation by seeds is the best technique to obtain an Adenium with a well-developed caudex from the start.
Please note: to harvest Adenium seeds, you must wait for the ripe fruits, which are pod-shaped, to dry and begin to open. Once harvested, they should be dried for a few days and sown quickly, as their seed viability decreases rapidly. However, outside of their natural habitat or a dedicated greenhouse (at a pinch!), seed production is extremely rare. Nevertheless, you can purchase them commercially.
- When to sow? Spring and summer are the ideal periods, as warmth promotes germination.
- How to do it?
- Soak the seeds in lukewarm water for 6 to 12 hours to speed up germination.
- Prepare a very well-draining medium composed of light potting soil, sand, and perlite.
- Place the seeds on the surface without burying them too deeply and lightly moisten.
- Place everything in a warm (25-30°C) and bright spot, under a greenhouse or a transparent cloche to retain moisture.
- Germination usually occurs within 7 to 14 days.
- Once the young plants are well established, gradually space out watering and transplant them into individual pots.
Propagation by cuttings (a faster method, but without a thick caudex)
Propagation by cuttings allows you to quickly obtain a new plant, but it will not have as aesthetically pleasing a caudex as one grown from seeds.
- When to take cuttings? In spring or summer, when the plant is in full growth.
- How to do it?
- Take a healthy stem at least 10 cm long, using a clean tool.
- Let the cutting dry for several days to prevent rot.
- Dip the base in cutting plant hormone powder (optional).
- Plant the stem in a very well-draining and slightly moist medium.
- Place in a bright and warm spot, without excess moisture.
- Rooting usually takes 4 to 6 weeks.
How to showcase a Desert Rose?
With its sculptural caudex and striking flowering, the Adenium fits perfectly into bright interiors with a minimalist, exotic, or bohemian style. It will thrive particularly in a modern and sleek décor, where its graphic shapes will be highlighted, or in a tropical-inspired interior, paired with other arid plants like cacti and succulents.
Which pot to choose?
To enhance its unique allure, it is best placed in:
- A raw terracotta pot, reminiscent of its natural medium and promoting good drainage.
- A matte ceramic designer pot, in neutral tones (white, beige, grey) for an elegant and contemporary look.
- A hanging or elevated pot, which will showcase its caudex and give an airy effect to the composition.
- A concrete pot, ideal for an industrial and minimalist décor.
What about in a terrarium?
The Adenium is not suited to closed terrariums, as it requires dry air and excellent ventilation. However, it can be placed in an open terrarium, such as a desert-style one, with sand, stones, and other succulents like haworthias or lithops. In this case, it is essential that the substrate is extremely well-draining and that watering remains very moderate.

Also see
- Discover our wide range of houseplants.
- There are many books on houseplants, but we recommend THE bible on the subject: The Encyclopaedia of Houseplants by Solène Moutardier, published by Ulmer.
- Subscribe!
- Contents
































Comments