
Lime - Citrus aurantifolia


Lime - Citrus aurantifolia


Lime - Citrus aurantifolia


Lime - Citrus aurantifolia
Lime - Citrus aurantifolia
Citrus x aurantiifolia
Key lime, Mexican lime, West Indian lime, Adam's apple, Key lime
Plant received in good condition and very well packaged. Thank you very much and I highly recommend. See you soon.
Anne Marie, 18/07/2020
Special offer!
Receive a €20 voucher for any order over €90 (excluding delivery costs, credit notes, and plastic-free options)!
1- Add your favorite plants to your cart.
2- Once you have reached €90, confirm your order (you can even choose the delivery date!).
3- As soon as your order is shipped, you will receive an email containing your voucher code, valid for 3 months (90 days).
Your voucher is unique and can only be used once, for any order with a minimum value of €20, excluding delivery costs.
Can be combined with other current offers, non-divisible and non-refundable.
Home or relay delivery (depending on size and destination)
Schedule delivery date,
and select date in basket
This plant carries a 6 months recovery warranty
More information
We guarantee the quality of our plants for a full growing cycle, and will replace at our expense any plant that fails to recover under normal climatic and planting conditions.
Description
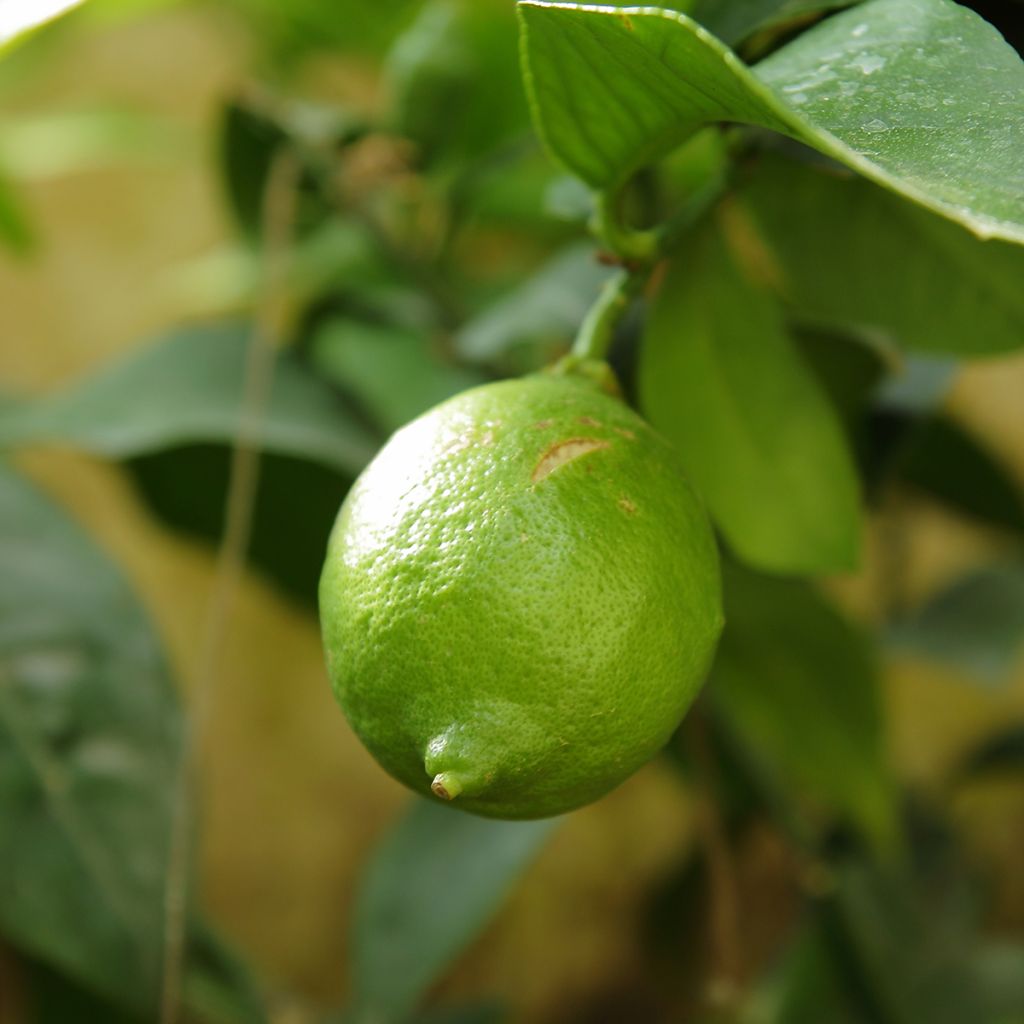
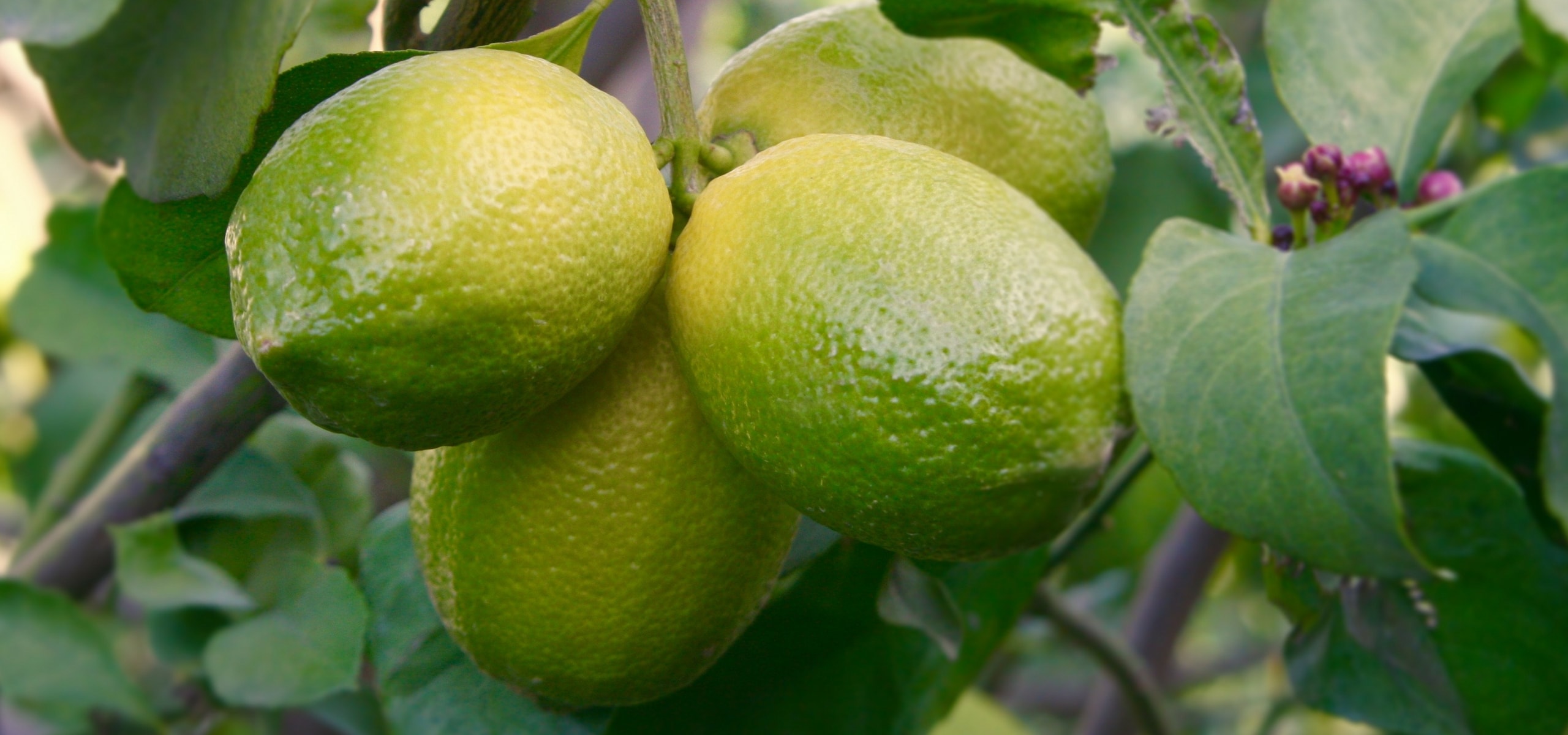
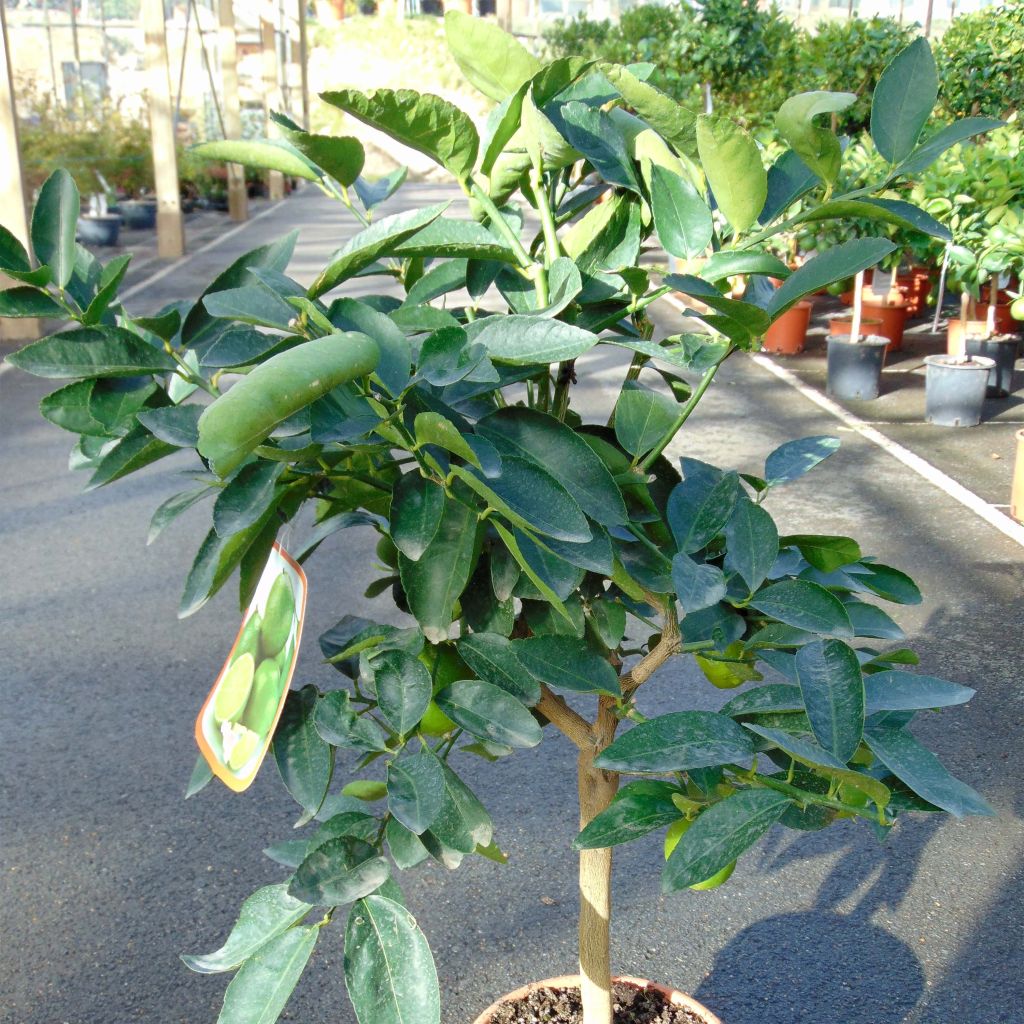
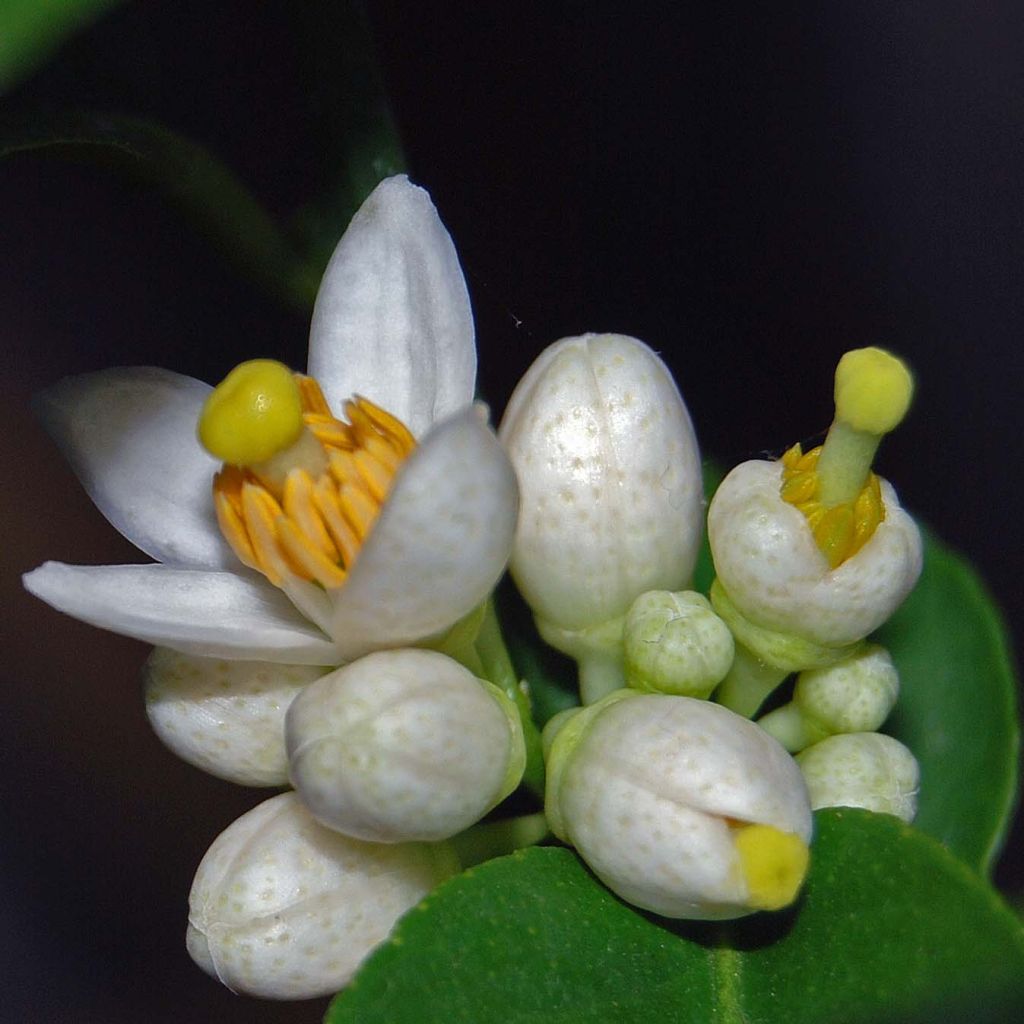
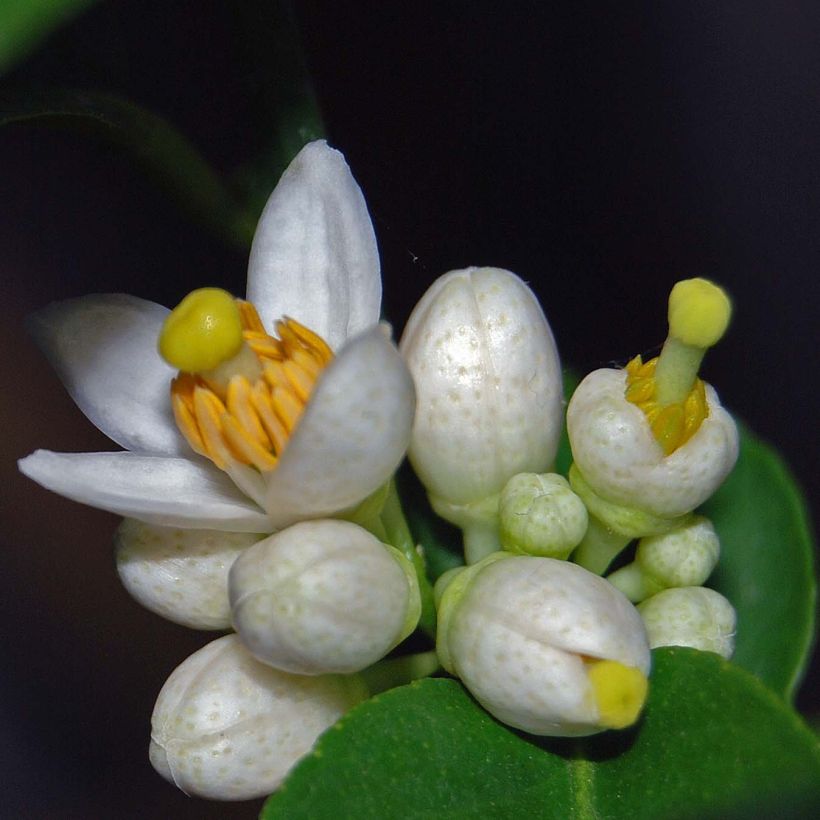
The Lime tree or Lime, in Latin Citrus aurantiifolia, is a moderately vigorous citrus tree, with a well-branched and ornamental habit, and highly floriferous in spring. Its small white star-shaped flowers, pleasantly scented, are followed by small fruits that are more or less spherical, covered with a smooth and thin skin, very fragrant when still dark green. The flesh of this citrus fruit is very juicy, particularly acidic but highly aromatic. This species, the least hardy of all citrus trees, has marked tropical requirements: it perishes below -3°C (26.6°F) and requires warmth throughout the year to fruit well. It can be grown in a large container and stored in a slightly heated greenhouse during winter, or planted in open ground in warm regions that are spared from frost.
Citrus aurantifolia is a spiny bush from the Rutaceae family, with a rather upright and bushy habit. It is believed to be originally from Southeast Asia, specifically from Malaysia and the Philippines, although its exact origin is a bit unclear. Recent studies tend to prove a hybrid origin between Citrus medica (citron) and C. micrantha (wild Philippine lime).
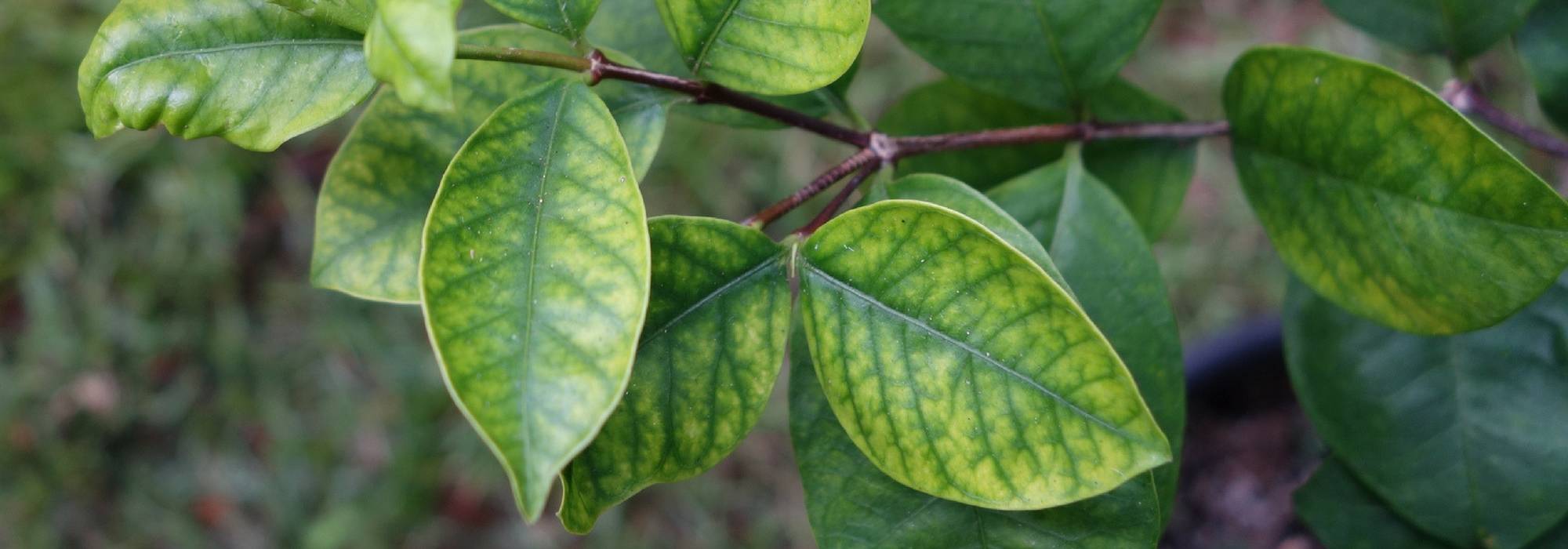
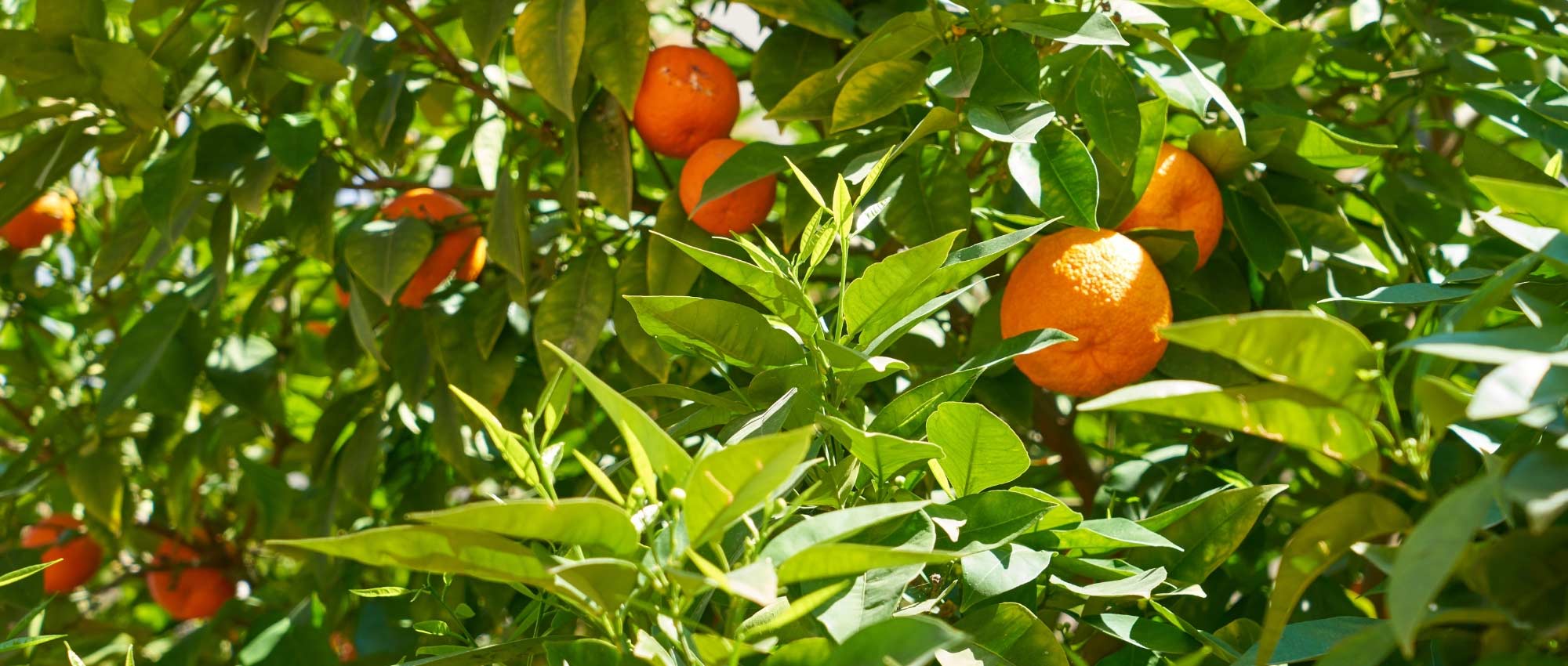
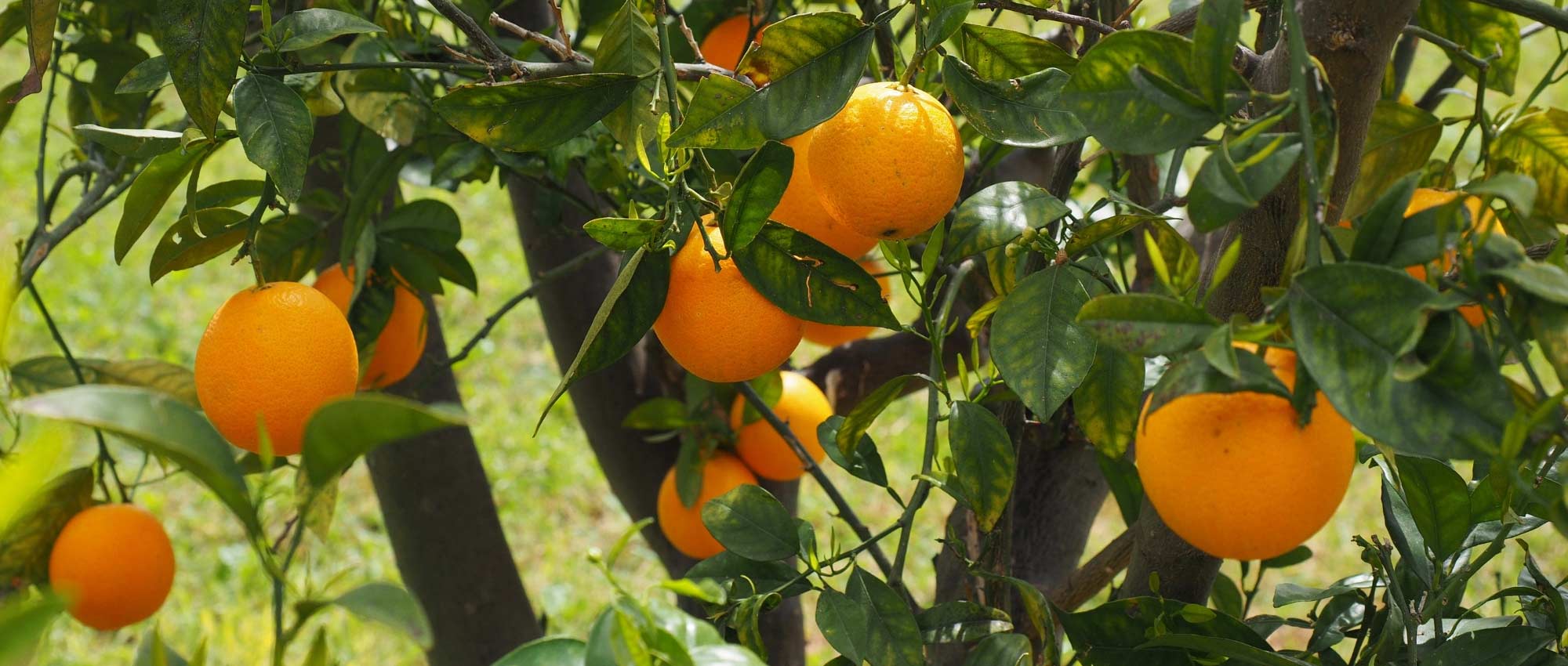
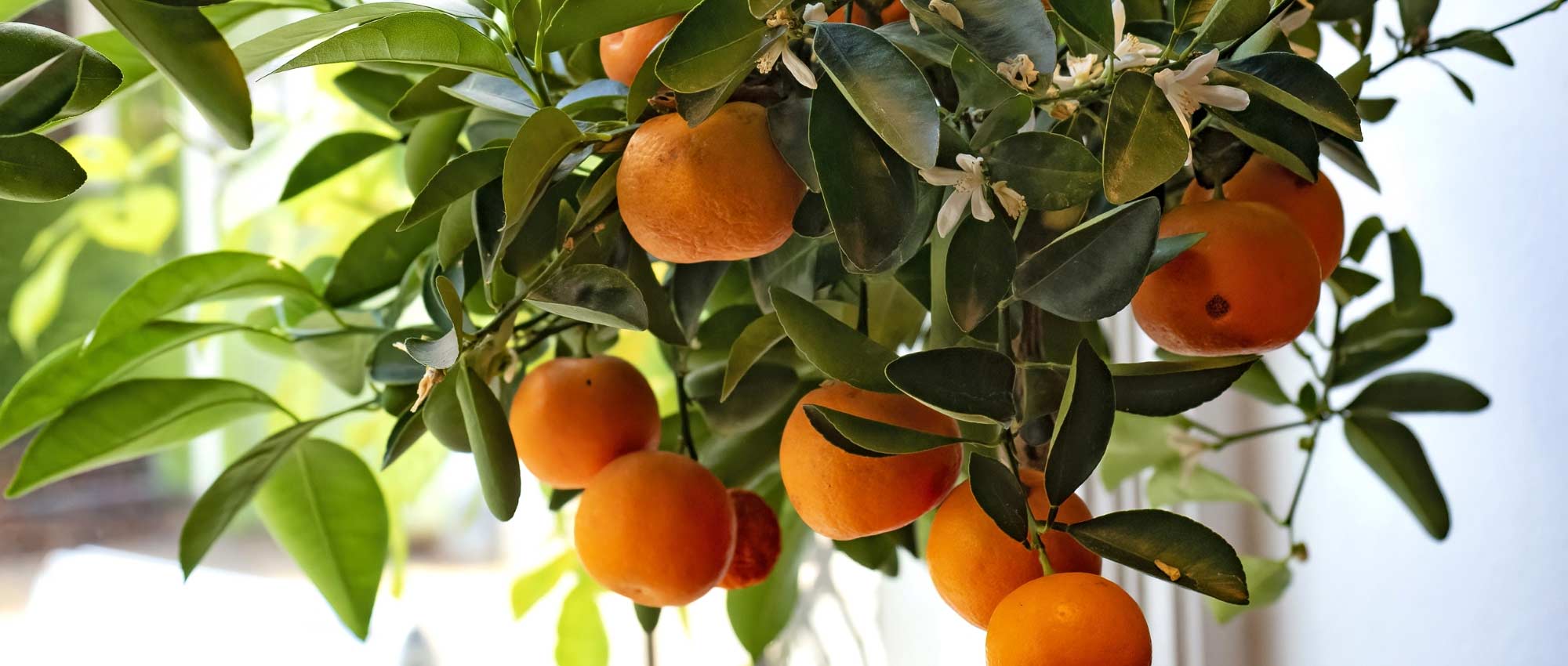
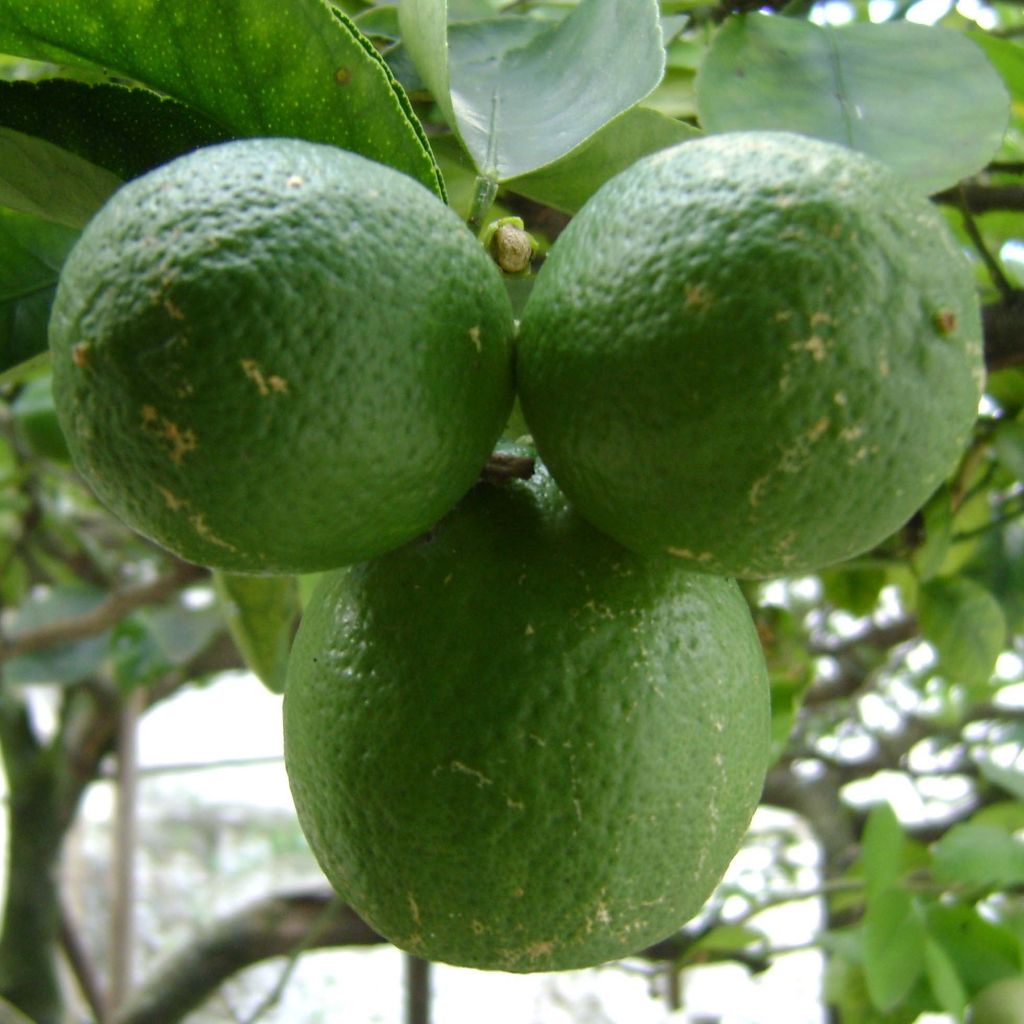
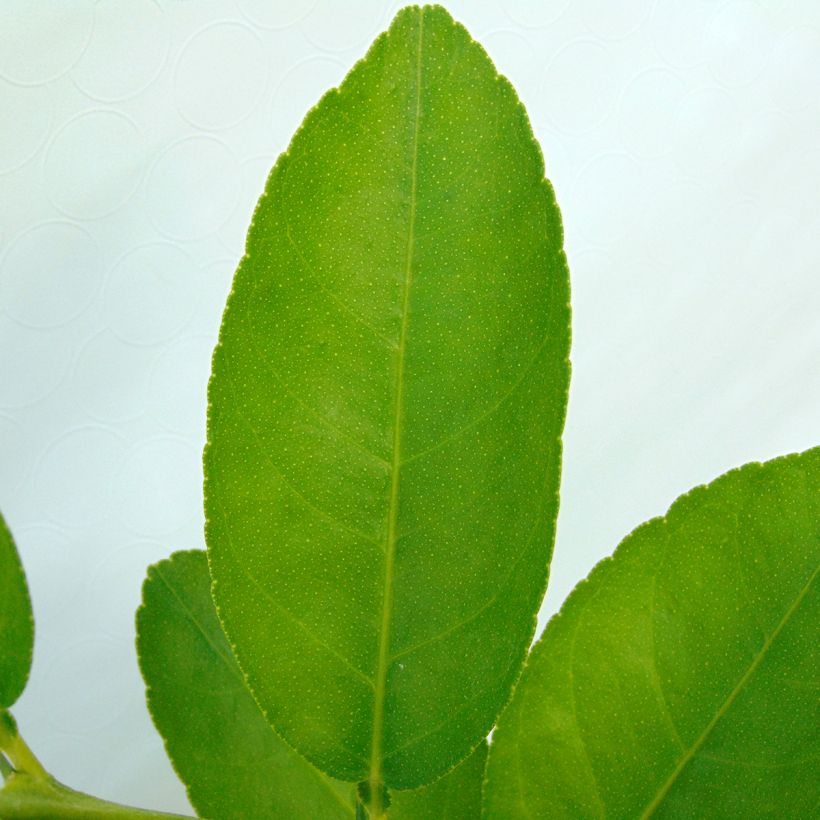
This small tree reaches a height of 3.50m (11ft) and spreads over approximately 2.50m (8ft). Its branches are short and carry numerous short and sharp thorns. Not very hardy, it can be planted in open ground along the narrow coastal strip of the Mediterranean. Elsewhere, it should be grown in a pot and stored at the first signs of cold weather. Primarily cultivated for its fruits, the lime tree blooms abundantly in March-April, and then sporadically until autumn in Mediterranean climates. It produces small white flowers, slightly tinged with yellow at the center, and with a sweet and delicious neroli fragrance, characteristic of citrus. These flowers give way to oval to rounded fruits, resembling yellow lemons, with a diameter of 3 to 5cm (1 to 2in). The very thin and smooth skin of the fruit is initially dark green and then turns green-yellow. The flesh of the fruit, white-green and translucent, is both very juicy and very acidic, and contains a few seeds. The fruits are harvested while still green, when their concentration of essential oils is at its peak. The evergreen and aromatic leaves of this citrus tree are ovate, leathery, small in size, and intensely green in colour.
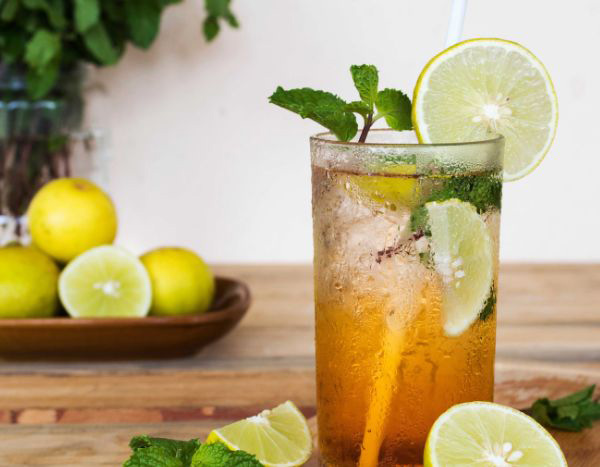
The fruits are part of the culinary traditions of several countries in Southeast Asia, as well as Reunion Island and the Caribbean. Its use is almost as extensive as that of yellow lemons, in savory or sweet dishes. Its juice is used in refreshing drinks or cocktails, adding a touch of acidity and a unique aroma. The zest is sometimes used to flavour pastries. Combined with a little chili, lime is often served with Reunionese dishes and Caribbean ti-punch. In addition to its culinary importance, the lime tree is also a medicinal plant whose therapeutic properties, used for centuries in traditional medicine, are now the subject of in-depth scientific research. Lime is less rich than lemon in ascorbic acid (Vitamin C), as well as in vitamins A and B. Easy to store, this citrus fruit was once loaded onto sailing ships, providing a good source of vitamins to fight against scurvy.
Like all Citrus, the lime tree contains visible essential oil sacs in its leaves, flowers, and fruits, which are extracted by distillation (flower and leaves) or by pressing (zest). The essential oil has rebalancing properties and is slightly sedative, helping to centre vital energies. Stimulating, the essential oil is known to facilitate blood circulation. The fragrance of the essential oil is described as fresh, lemony, tangy, with slightly sweet and bitter notes.
Most citrus trees thrive in open ground in Mediterranean coastal regions, where they find the necessary warmth all year round. To fruit well, they must not lack water or nutrients. Not very hardy, the Citrus aurantifolia starts to suffer from cold temperatures below 0°C (32°F). It is a self-fertile bush, which means that a single individual is sufficient for complete pollination and fruiting.
Lime - Citrus aurantifolia in pictures
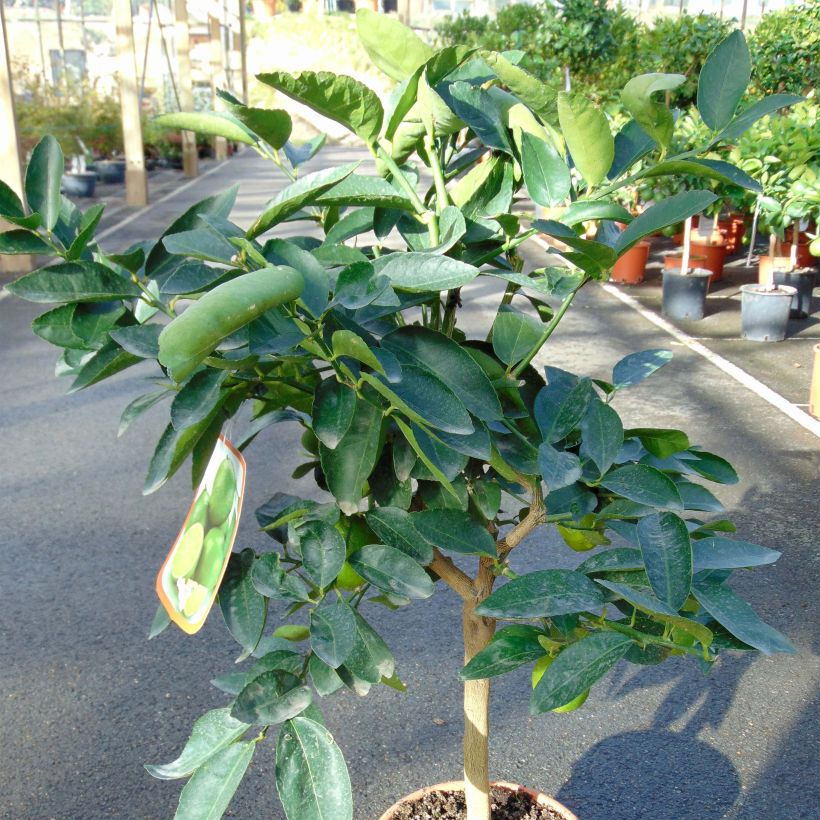






Plant habit
Fruit
Flowering
Foliage
Botanical data
Citrus
x aurantiifolia
Rutaceae
Key lime, Mexican lime, West Indian lime, Adam's apple, Key lime
Southeast Asia
Planting and care
Plant in open ground: The citrus tree appreciates neutral, slightly acidic, and non-calcareous soils. It is reasonable to plant it in open ground only if you reside on a highly favorable Mediterranean coastal strip, spared from frost, as the hardiness of this citrus tree does not exceed -3°C (26.6°F) and it requires a lot of heat to bloom and bear fruit. The best period to carry out your planting is in early spring, in March and April. Be careful not to bury the collar. Citrus trees are naturally greedy and require water to bear fruit well: in all cases, consider amending with well-decomposed compost or "special citrus" fertilizer. Choose a sunny but not scorching spot for your bush in a sheltered location from the wind to prevent the foliage from drying out and causing the young fruits to fall off. Place it in a location protected from sea spray.
Planting in a pot: In all other regions, the Citrus tree will be planted in a pot that you can keep in a slightly heated greenhouse or conservatory, frost-free, in an atmosphere that is not too dry. It will appreciate being outdoors in summer. Planting in a pot or repotting takes place at the end of summer. Choose a pot slightly larger than the root system, as citrus trees do not like to feel cramped. Moisten the root ball well. To improve the drainage capabilities of the mixture, line the bottom of the pot with clay balls. Loosen the root ball and mix two-thirds garden soil with one-third 'special citrus' potting soil. Water generously. Prefer pots made of terracotta or breathable material.
Citrus trees need a lot of water to thrive. Your citrus tree should be watered daily with low or non-calcareous water, and the soil should remain consistently moist. Similarly, make sure to regularly provide it with the fertiliser it needs: every 6 months for slow-release granular fertiliser or every 3 waterings for liquid fertiliser.
Planting period
Intended location
Care
Planting & care advice
-
, onOrder confirmed
Reply from on Promesse de fleurs
Similar products
Haven't found what you were looking for?
Hardiness is the lowest winter temperature a plant can endure without suffering serious damage or even dying. However, hardiness is affected by location (a sheltered area, such as a patio), protection (winter cover) and soil type (hardiness is improved by well-drained soil).
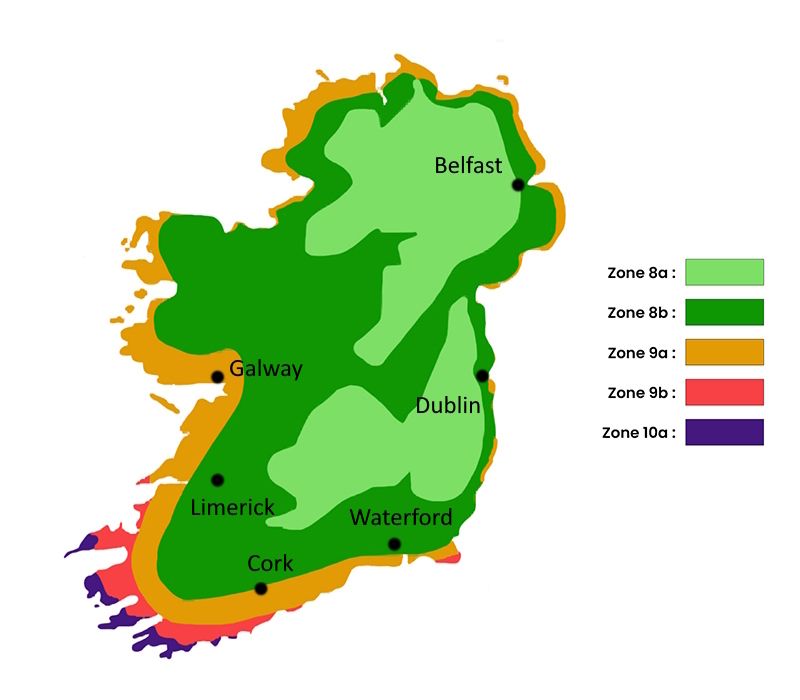
Photo Sharing Terms & Conditions
In order to encourage gardeners to interact and share their experiences, Promesse de fleurs offers various media enabling content to be uploaded onto its Site - in particular via the ‘Photo sharing’ module.
The User agrees to refrain from:
- Posting any content that is illegal, prejudicial, insulting, racist, inciteful to hatred, revisionist, contrary to public decency, that infringes on privacy or on the privacy rights of third parties, in particular the publicity rights of persons and goods, intellectual property rights, or the right to privacy.
- Submitting content on behalf of a third party;
- Impersonate the identity of a third party and/or publish any personal information about a third party;
In general, the User undertakes to refrain from any unethical behaviour.
All Content (in particular text, comments, files, images, photos, videos, creative works, etc.), which may be subject to property or intellectual property rights, image or other private rights, shall remain the property of the User, subject to the limited rights granted by the terms of the licence granted by Promesse de fleurs as stated below. Users are at liberty to publish or not to publish such Content on the Site, notably via the ‘Photo Sharing’ facility, and accept that this Content shall be made public and freely accessible, notably on the Internet.
Users further acknowledge, undertake to have ,and guarantee that they hold all necessary rights and permissions to publish such material on the Site, in particular with regard to the legislation in force pertaining to any privacy, property, intellectual property, image, or contractual rights, or rights of any other nature. By publishing such Content on the Site, Users acknowledge accepting full liability as publishers of the Content within the meaning of the law, and grant Promesse de fleurs, free of charge, an inclusive, worldwide licence for the said Content for the entire duration of its publication, including all reproduction, representation, up/downloading, displaying, performing, transmission, and storage rights.
Users also grant permission for their name to be linked to the Content and accept that this link may not always be made available.
By engaging in posting material, Users consent to their Content becoming automatically accessible on the Internet, in particular on other sites and/or blogs and/or web pages of the Promesse de fleurs site, including in particular social pages and the Promesse de fleurs catalogue.
Users may secure the removal of entrusted content free of charge by issuing a simple request via our contact form.
The flowering period indicated on our website applies to countries and regions located in USDA zone 8 (France, the United Kingdom, Ireland, the Netherlands, etc.)
It will vary according to where you live:
- In zones 9 to 10 (Italy, Spain, Greece, etc.), flowering will occur about 2 to 4 weeks earlier.
- In zones 6 to 7 (Germany, Poland, Slovenia, and lower mountainous regions), flowering will be delayed by 2 to 3 weeks.
- In zone 5 (Central Europe, Scandinavia), blooming will be delayed by 3 to 5 weeks.
In temperate climates, pruning of spring-flowering shrubs (forsythia, spireas, etc.) should be done just after flowering.
Pruning of summer-flowering shrubs (Indian Lilac, Perovskia, etc.) can be done in winter or spring.
In cold regions as well as with frost-sensitive plants, avoid pruning too early when severe frosts may still occur.
The planting period indicated on our website applies to countries and regions located in USDA zone 8 (France, United Kingdom, Ireland, Netherlands).
It will vary according to where you live:
- In Mediterranean zones (Marseille, Madrid, Milan, etc.), autumn and winter are the best planting periods.
- In continental zones (Strasbourg, Munich, Vienna, etc.), delay planting by 2 to 3 weeks in spring and bring it forward by 2 to 4 weeks in autumn.
- In mountainous regions (the Alps, Pyrenees, Carpathians, etc.), it is best to plant in late spring (May-June) or late summer (August-September).
The harvesting period indicated on our website applies to countries and regions in USDA zone 8 (France, England, Ireland, the Netherlands).
In colder areas (Scandinavia, Poland, Austria...) fruit and vegetable harvests are likely to be delayed by 3-4 weeks.
In warmer areas (Italy, Spain, Greece, etc.), harvesting will probably take place earlier, depending on weather conditions.
The sowing periods indicated on our website apply to countries and regions within USDA Zone 8 (France, UK, Ireland, Netherlands).
In colder areas (Scandinavia, Poland, Austria...), delay any outdoor sowing by 3-4 weeks, or sow under glass.
In warmer climes (Italy, Spain, Greece, etc.), bring outdoor sowing forward by a few weeks.














































