
Melilotus officinalis - seeds


Melilotus officinalis - seeds


Melilotus officinalis - seeds


Melilotus officinalis - seeds
Melilotus officinalis - seeds
Melilotus officinalis
Yellow sweet clover, common melilot, ribbed melilot, yellow melilot
Special offer!
Receive a €20 voucher for any order over €90 (excluding delivery costs, credit notes, and plastic-free options)!
1- Add your favorite plants to your cart.
2- Once you have reached €90, confirm your order (you can even choose the delivery date!).
3- As soon as your order is shipped, you will receive an email containing your voucher code, valid for 3 months (90 days).
Your voucher is unique and can only be used once, for any order with a minimum value of €20, excluding delivery costs.
Can be combined with other current offers, non-divisible and non-refundable.
Home or relay delivery (depending on size and destination)
Schedule delivery date,
and select date in basket
This plant carries a 6 months recovery warranty
More information
We guarantee the quality of our plants for a full growing cycle, and will replace at our expense any plant that fails to recover under normal climatic and planting conditions.
Description
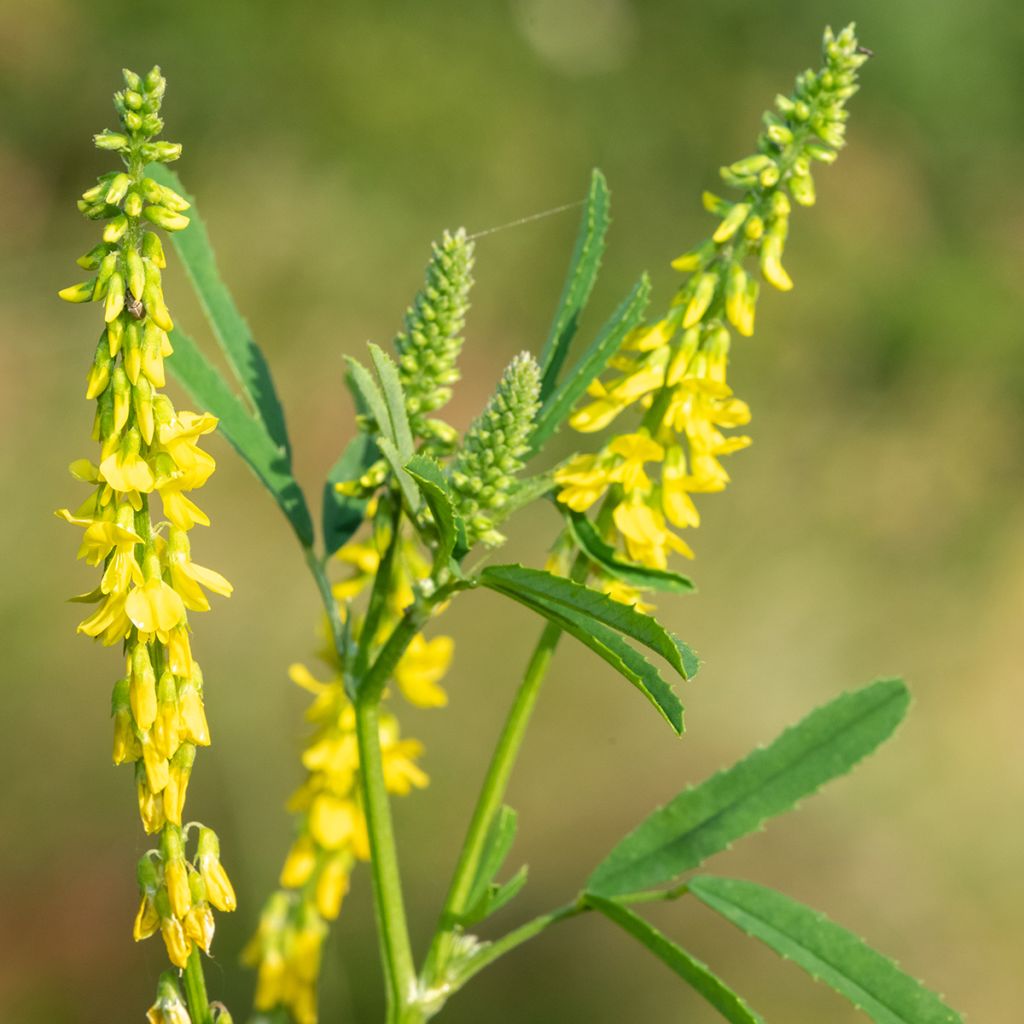
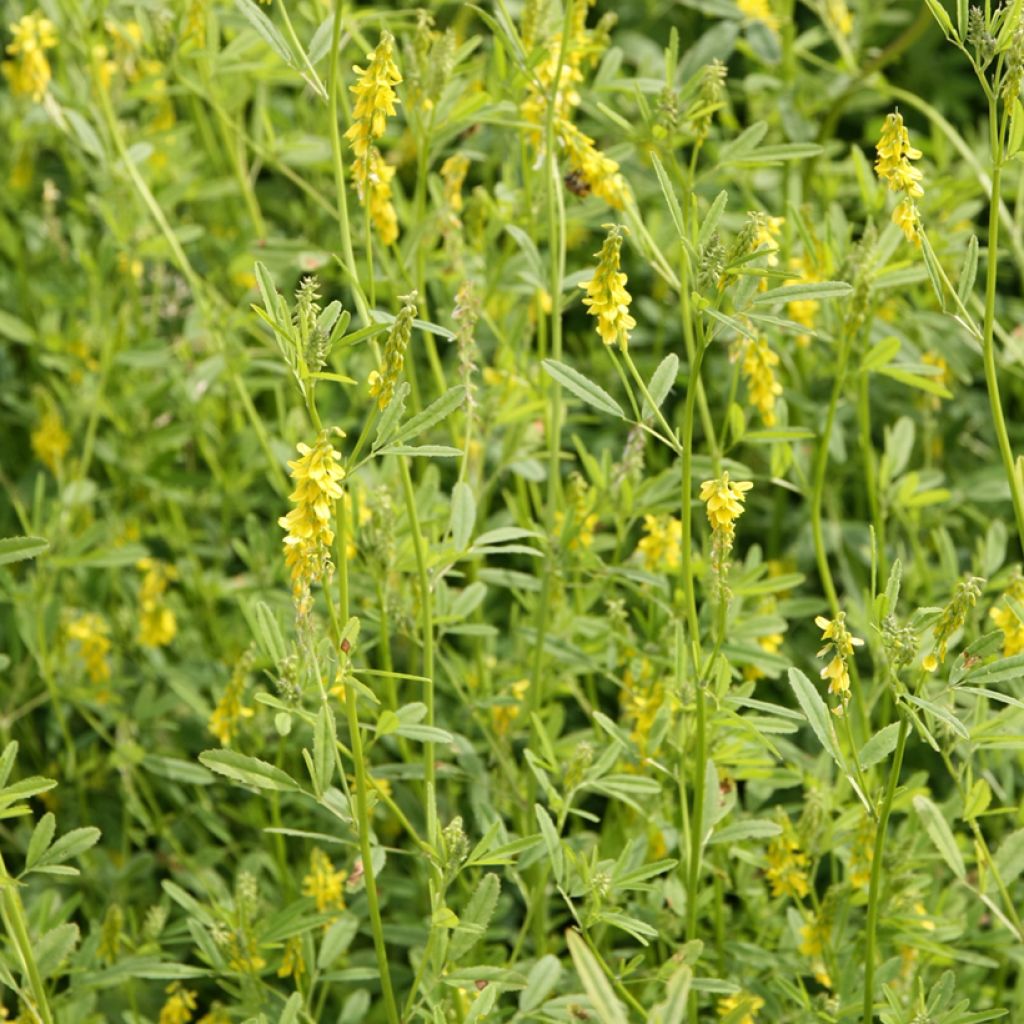
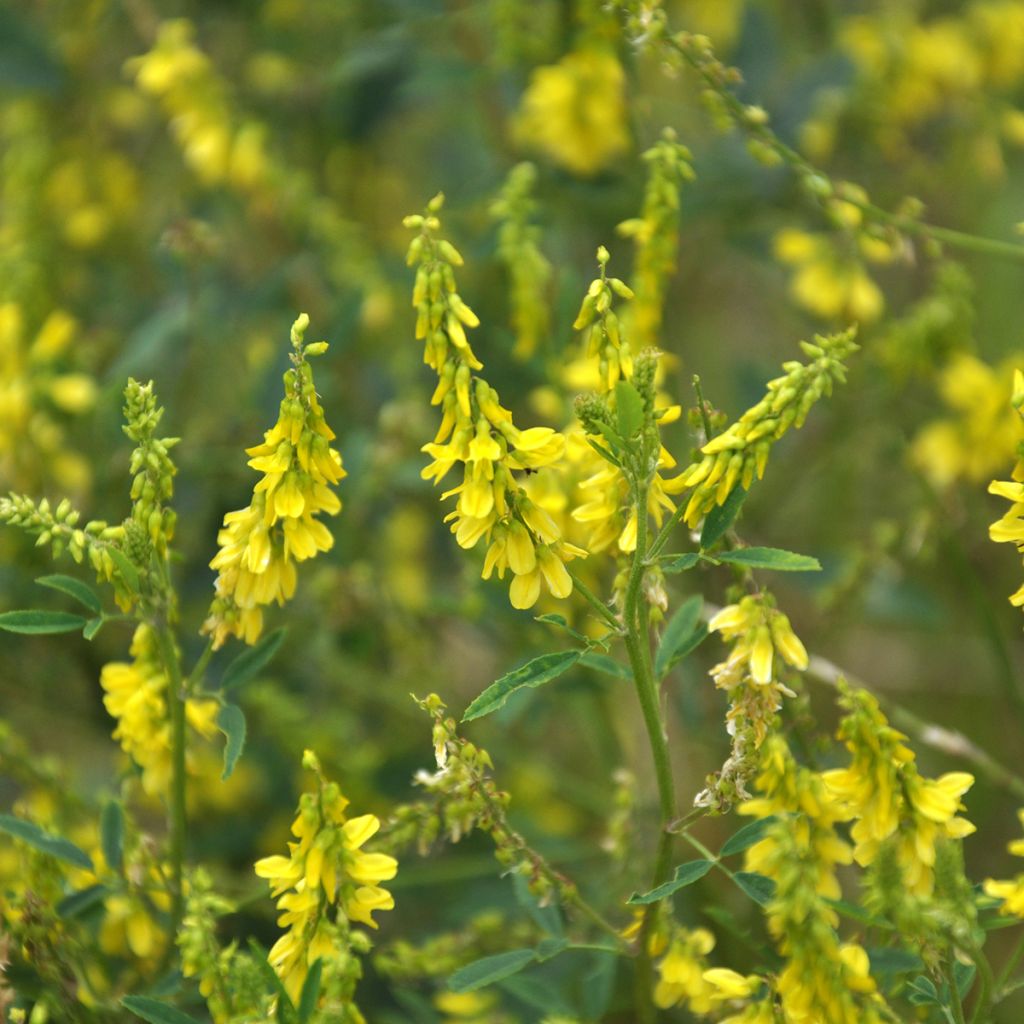
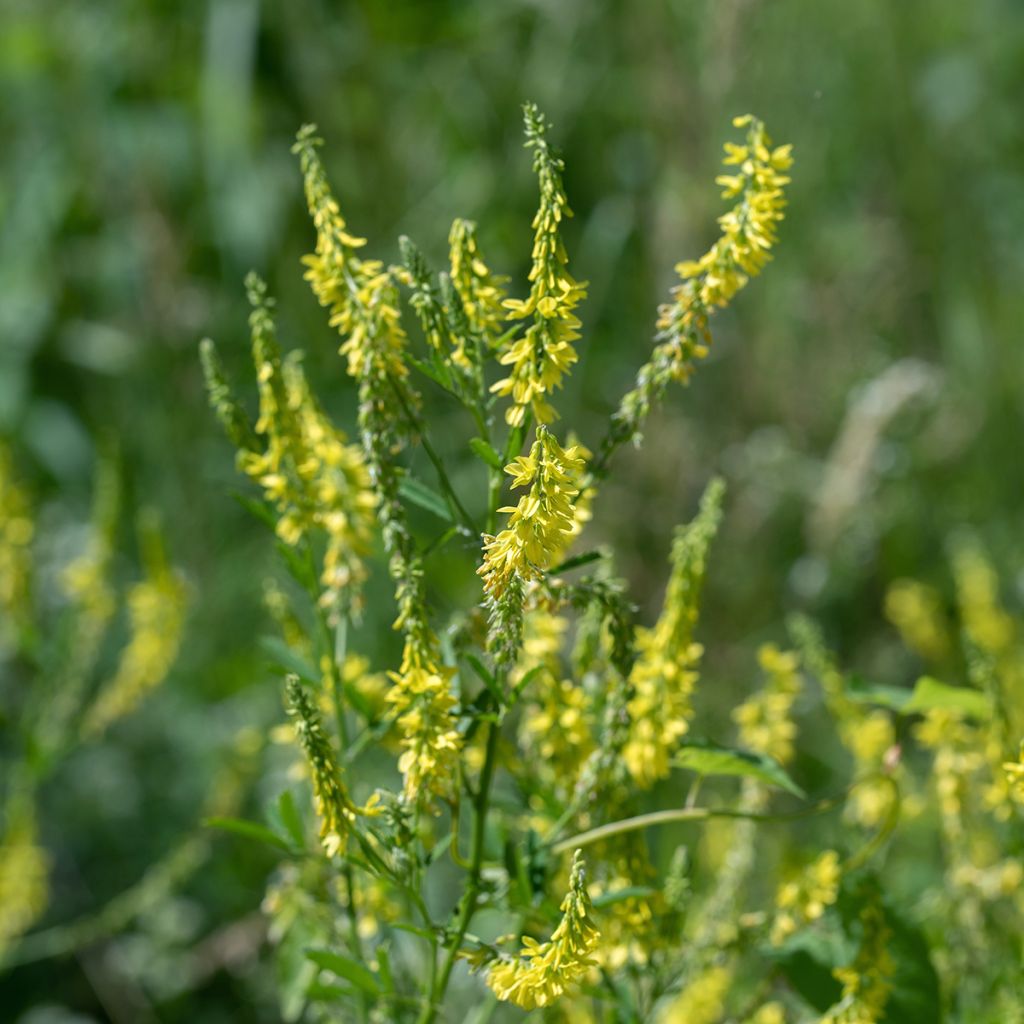
Yellow Sweet Clover, known by its Latin name Melilotus officinalis, is an annual or biennial herbaceous plant. Characterised by a yellow summer flowering, trifoliate leaves, and a taproot, it is used as a nitrogen-fixing forage plant and green manure, a nectar-rich plant loved by bees, providing beekeepers with excellent honey yields. It is also an edible plant. It grows in all types of soil, even very dry ones. The only conditions that are not suitable for it are shade and acidic soils.
Yellow Sweet Clover or Melilotus officinal belongs to the Fabaceae family (formerly legumes). It is widespread in the plains of temperate regions in Europe. It grows in limestone clearings, lightly wooded cliffs, meadows and weed-infested fields, as well as in open and disturbed sites, riparian zones, meadows, pastures, roadsides, ditches, vacant lots, and fallow land. It is a nectar-rich herbaceous plant, reaching a height of 30 cm to 1.20 m, depending on the growing conditions, with leaves composed of 3 leaflets. The light green stems are round or slightly furrowed and often branched. The alternate leaves are trifoliate and scattered along the stem. The upper stems end in narrow racemes of yellow flowers that tend to hang down from the central peduncle of the raceme. Each flower is about 8.5 mm long and consists of 5 yellow petals and a light green calyx with 5 teeth. The flowers are small, soft, tubular at the base, and widen towards the outer edges. Its flower clusters appear from June to September. The plants usually flower and die in the second year of growth. The Yellow Sweet Clover is cold-resistant down to -15°C. It has deep roots, which help to loosen the soil.
Melilotus officinalis is adapted to a wide range of climatic conditions and grows in practically all types of soils, including very poor soils. It prefers soils with a neutral pH or a tendency towards limestone. It only needs adequate moisture during germination. It is then capable of growing in extremely dry conditions. It can be invasive, so it is important to remove the flowers before they seed. This plant nourishes and improves the soil by providing it with various nutrients and stimulating soil microbial life. Its roots loosen and aerate the soil. Used as green manure, it also protects soils from leaching (nutrient loss in sandy soil), rain compaction (formation of a crust in loamy soil), and erosion (caused by runoff in case of heavy rain on sloping terrain). This vegetative cover also helps to limit weed growth by preventing the growth of unwanted plants. Green manures are sown on uncultivated plots or between rows of vegetables. They are either naturally destroyed by frost or cut before seed formation. Once destroyed, they can be left in place as mulch, or crushed and incorporated into the top layers of the soil, or collected and added to compost.
Yellow Sweet Clover is an edible plant rich in vitamin C, with leaves that emit a sweet smell reminiscent of hay, derived from coumarin. Its young leaves can be eaten raw in small quantities in salads, and its seeds can be used as a spice. Although Yellow Sweet Clover has medicinal properties, it is strongly advised not to harvest it for self-use as a "treatment" and not to dry it oneself. Improperly dried coumarin transforms into dicoumarol, a highly toxic compound. It is an antispasmodic, antiseptic, and diuretic. It is also used to aid sleep and calm nervousness. Consumed in very high doses, sweet clover can be toxic.
Harvest
Plant habit
Foliage
Botanical data
Melilotus
officinalis
Fabaceae
Yellow sweet clover, common melilot, ribbed melilot, yellow melilot
Melilotus arvensis, Melilotus vulgaris, Melilotus officinalis var. micranthus, Trifolium officinale
Central Europe
Perennial
Other Green fertilisers
View all →Planting and care
Sowing takes place in spring. Yellow Sweet Clover prefers soils with a neutral pH or a tendency towards limestone.
If your soil is compact, dig it to allow the long roots of the Sweet Clover to establish themselves. Similarly, remove as many unwanted weeds as possible before sowing to allow for good germination.
Sow by broadcasting, cover the seeds with soil by raking. Firm the soil with the back of the rake and water lightly.
Yellow Sweet Clover does not require any particular maintenance during cultivation, or watering.
Seedlings
Care
Intended location
Planting & care advice
This item has not been reviewed yet - be the first to leave a review about it.
Similar products
Haven't found what you were looking for?
Hardiness is the lowest winter temperature a plant can endure without suffering serious damage or even dying. However, hardiness is affected by location (a sheltered area, such as a patio), protection (winter cover) and soil type (hardiness is improved by well-drained soil).
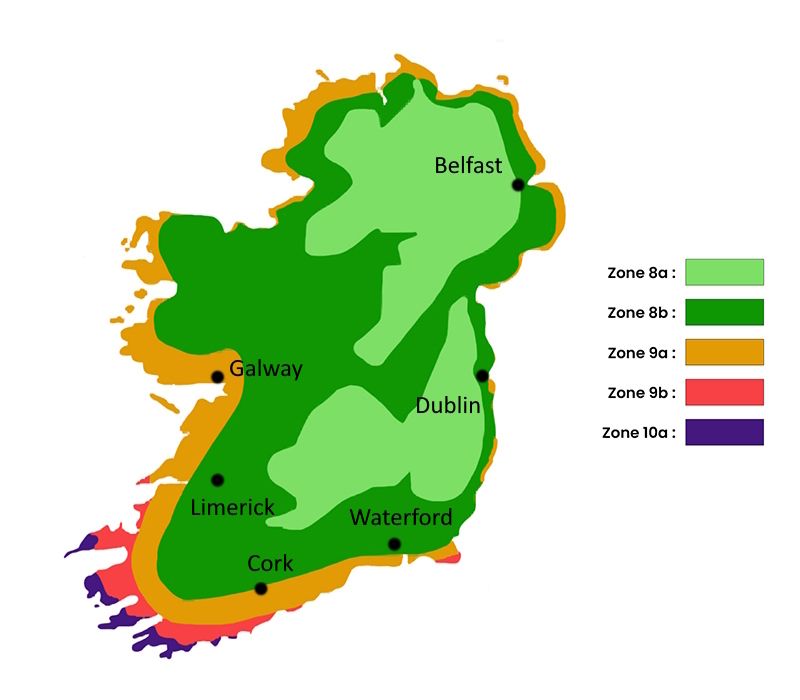
Photo Sharing Terms & Conditions
In order to encourage gardeners to interact and share their experiences, Promesse de fleurs offers various media enabling content to be uploaded onto its Site - in particular via the ‘Photo sharing’ module.
The User agrees to refrain from:
- Posting any content that is illegal, prejudicial, insulting, racist, inciteful to hatred, revisionist, contrary to public decency, that infringes on privacy or on the privacy rights of third parties, in particular the publicity rights of persons and goods, intellectual property rights, or the right to privacy.
- Submitting content on behalf of a third party;
- Impersonate the identity of a third party and/or publish any personal information about a third party;
In general, the User undertakes to refrain from any unethical behaviour.
All Content (in particular text, comments, files, images, photos, videos, creative works, etc.), which may be subject to property or intellectual property rights, image or other private rights, shall remain the property of the User, subject to the limited rights granted by the terms of the licence granted by Promesse de fleurs as stated below. Users are at liberty to publish or not to publish such Content on the Site, notably via the ‘Photo Sharing’ facility, and accept that this Content shall be made public and freely accessible, notably on the Internet.
Users further acknowledge, undertake to have ,and guarantee that they hold all necessary rights and permissions to publish such material on the Site, in particular with regard to the legislation in force pertaining to any privacy, property, intellectual property, image, or contractual rights, or rights of any other nature. By publishing such Content on the Site, Users acknowledge accepting full liability as publishers of the Content within the meaning of the law, and grant Promesse de fleurs, free of charge, an inclusive, worldwide licence for the said Content for the entire duration of its publication, including all reproduction, representation, up/downloading, displaying, performing, transmission, and storage rights.
Users also grant permission for their name to be linked to the Content and accept that this link may not always be made available.
By engaging in posting material, Users consent to their Content becoming automatically accessible on the Internet, in particular on other sites and/or blogs and/or web pages of the Promesse de fleurs site, including in particular social pages and the Promesse de fleurs catalogue.
Users may secure the removal of entrusted content free of charge by issuing a simple request via our contact form.
The flowering period indicated on our website applies to countries and regions located in USDA zone 8 (France, the United Kingdom, Ireland, the Netherlands, etc.)
It will vary according to where you live:
- In zones 9 to 10 (Italy, Spain, Greece, etc.), flowering will occur about 2 to 4 weeks earlier.
- In zones 6 to 7 (Germany, Poland, Slovenia, and lower mountainous regions), flowering will be delayed by 2 to 3 weeks.
- In zone 5 (Central Europe, Scandinavia), blooming will be delayed by 3 to 5 weeks.
In temperate climates, pruning of spring-flowering shrubs (forsythia, spireas, etc.) should be done just after flowering.
Pruning of summer-flowering shrubs (Indian Lilac, Perovskia, etc.) can be done in winter or spring.
In cold regions as well as with frost-sensitive plants, avoid pruning too early when severe frosts may still occur.
The planting period indicated on our website applies to countries and regions located in USDA zone 8 (France, United Kingdom, Ireland, Netherlands).
It will vary according to where you live:
- In Mediterranean zones (Marseille, Madrid, Milan, etc.), autumn and winter are the best planting periods.
- In continental zones (Strasbourg, Munich, Vienna, etc.), delay planting by 2 to 3 weeks in spring and bring it forward by 2 to 4 weeks in autumn.
- In mountainous regions (the Alps, Pyrenees, Carpathians, etc.), it is best to plant in late spring (May-June) or late summer (August-September).
The harvesting period indicated on our website applies to countries and regions in USDA zone 8 (France, England, Ireland, the Netherlands).
In colder areas (Scandinavia, Poland, Austria...) fruit and vegetable harvests are likely to be delayed by 3-4 weeks.
In warmer areas (Italy, Spain, Greece, etc.), harvesting will probably take place earlier, depending on weather conditions.
The sowing periods indicated on our website apply to countries and regions within USDA Zone 8 (France, UK, Ireland, Netherlands).
In colder areas (Scandinavia, Poland, Austria...), delay any outdoor sowing by 3-4 weeks, or sow under glass.
In warmer climes (Italy, Spain, Greece, etc.), bring outdoor sowing forward by a few weeks.
























































